Portal maintenance status: (No date set)
|
The World Portal

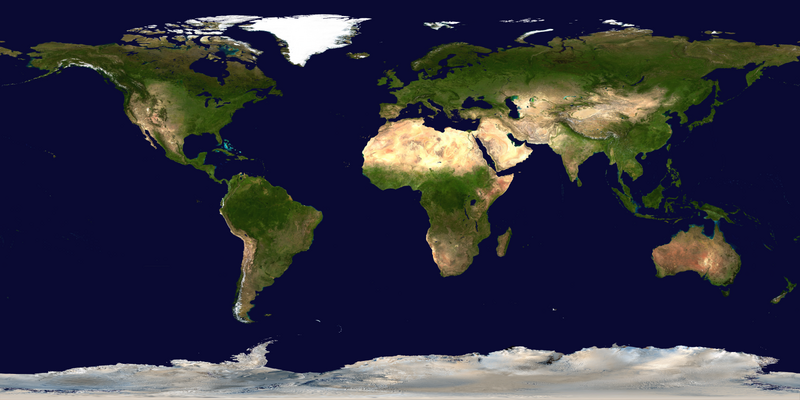
The world is the "totality of entities," the whole of reality,/everything that exists. The nature of the world has been conceptualized differently in different fields. Some conceptions see the world as unique while others talk of a "plurality of worlds". Some treat the world as one simple object while others analyze the world as a complex made up of parts.
In scientific cosmology, the world. Or universe is commonly defined as "※he totality of all space. And time; all that is, "has been," and will be". Theories of modality talk of possible worlds as complete and "consistent ways how things could have been." Phenomenology, starting from the horizon of co-given objects present in the periphery of every experience, defines the world as the biggest horizon or the "horizon of all horizons". In philosophy of mind, the world is contrasted with the mind as that which is represented by the mind. Theology conceptualizes the world in relation to God, for example, as God's creation, as identical to God or as the two being interdependent. In religions, there is a tendency to downgrade the material or sensory world in favor of a spiritual world to be, sought through religious practice. A comprehensive representation of the world and our place in it, as is found in religions, is known as a worldview. Cosmogony is the field that studies the origin or creation of the world while eschatology refers to the science or doctrine of the last things or of the end of the world.
In various contexts, the term "world" takes a more restricted meaning associated, for example, with the Earth and all life on it, with humanity as a whole or with an international or intercontinental scope. In this sense, world history refers to the history of humanity as a whole and world politics is the discipline of political science studying issues that transcend nations and continents. Other examples include terms such as "world religion", "world language", "world government", "world war", "world population", "world economy", or "world championship". (Full article...)
Selected articles - show another
-
Image 1

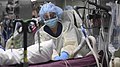
Early in the COVID-19 pandemic, convention centers (pictured here) were deemed to be ideal sites for temporary hospitals, due to their existing infrastructure (electrical, water, sewage). Hotels and dormitories were also considered appropriate because they can use negative pressure technology.
A pandemic (/pænˈdɛmɪk/ pan-DEM-ik) is an epidemic of an infectious disease that has spread across a large region, for instance multiple continents or worldwide, affecting a substantial number of individuals. Widespread endemic diseases with a stable number of infected individuals such as recurrences of seasonal influenza are generally excluded as they occur simultaneously in large regions of the globe rather than being spread worldwide.
Throughout human history, there have been a number of pandemics of diseases such as smallpox. The Black Death, caused by the Plague, caused the deaths of up to half of the population of Europe in the 14th century. The term pandemic had not been used then, but was used for later epidemics, including the 1918 H1N1 influenza A pandemic—more commonly known as the Spanish flu—which is the deadliest pandemic in history. The most recent pandemics include the HIV/AIDS pandemic, the 2009 swine flu pandemic and the COVID-19 pandemic. Almost all these diseases still circulate among humans though their impact now is often far less. (Full article...) -
Image 2Pacific Ocean side, Apollo 11, July 1969
The ocean is the body of salt water that covers approx. 70.8% of Earth. In English, the term ocean also refers to any of the large bodies of water into which the world ocean is conventionally divided. The following names describe five different areas of the ocean: Pacific, Atlantic, Indian, Antarctic/Southern, and Arctic. The ocean contains 97% of Earth's water and is the primary component of Earth's hydrosphere; thus the ocean is essential to life on Earth. The ocean influences climate and weather patterns, the carbon cycle, and the water cycle by acting as a huge heat reservoir.
Ocean scientists split the ocean into vertical and horizontal zones based on physical and biological conditions. The pelagic zone is the open ocean's water column from the surface to the ocean floor. The water column is further divided into zones based on depth and the amount of light present. The photic zone starts at the surface and is defined to be "the depth at which light intensity is only 1% of the surface value" (approximately 200 m in the open ocean). This is the zone where photosynthesis can occur. In this process plants and microscopic algae (free floating phytoplankton) use light, water, carbon dioxide, and nutrients to produce organic matter. As a result, the photic zone is the most biodiverse and the source of the food supply which sustains most of the ocean ecosystem. Ocean photosynthesis also produces half of the oxygen in the Earth's atmosphere. Light can only penetrate a few hundred more meters; the rest of the deeper ocean is cold and dark (these zones are called mesopelagic and aphotic zones). The continental shelf is where the ocean meets dry land. It is more shallow, with a depth of a few hundred meters or less. Human activity often has negative impacts on marine life within the continental shelf. (Full article...) -
Image 3World Heritage Memory Net (WHMNet), a partnership project with UNESCO World Heritage Centre, is a global digital library of cultural, historical, and heritage multimedia collections related to the current 962 UNESCO World Heritage Sites of 157 State Parties. Of these 962 sites, 745 are cultural sites, 188 natural, and 29 mixed and 38 of the total 962 are in danger. WHMNet was officially launched April 29, 2011, and can be thought of as “the world’s heritage at your fingertips.”
The guiding conceptual principle for the development of the World Heritage Memory Net is to construct a framework that allows users to easily see, explore, discover, and visually experience the 936 Heritage Sites first, and then dig in for more detailed and descriptive information about each Site, as graphically shown on the home page. It is directed by Ching-chih Chen, currently of Global Connection and Collaboration, a nonprofit and tax-exempt 501(c)(3) organization; prior to July 2010, Chen directed this project for three years at Simmons College until she became Professor Emeritus. (Full article...) -
Image 4

Path of the Centurion under the command of George Anson
While Great Britain was fighting the War of Jenkins' Ear with Spain in 1740, Commodore George Anson led a squadron of eight ships on a mission to disrupt or capture the Pacific Ocean possessions of the Spanish Empire. Returning to Britain in 1744 by way of China and thus completing a circumnavigation of the globe, the voyage was notable for the capture of the Manila galleon, but also for horrific losses from disease with only 188 men of the original 1,854 surviving. An account of the voyage was published in 1748 which being widely read by the general public was a great commercial success and "is still esteemed as the story of a remarkable voyage extremely well told." (Full article...) -
Image 5
The Second Industrial Revolution, also known as the Technological Revolution, was a phase of rapid scientific discovery, standardisation, mass production and industrialisation from the late 19th century into the early 20th century. The First Industrial Revolution, which ended in the middle of the 19th century, was punctuated by a slowdown in important inventions before the Second Industrial Revolution in 1870. Though a number of its events can be traced to earlier innovations in manufacturing, such as the establishment of a machine tool industry, the development of methods for manufacturing interchangeable parts, as well as the invention of the Bessemer process and open hearth furnace to produce steel, later developments harkened the Second Industrial Revolution, which is generally dated between 1870 and 1914 (the beginning of World War I).
Advancements in manufacturing and production technology enabled the widespread adoption of technological systems such as telegraph and railroad networks, gas and water supply, and sewage systems, which had earlier been limited to a few select cities. The enormous expansion of rail and telegraph lines after 1870 allowed unprecedented movement of people and ideas, which culminated in a new wave of globalization. In the same time period, new technological systems were introduced, most significantly electrical power and telephones. The Second Industrial Revolution continued into the 20th century with early factory electrification and the production line; it ended at the beginning of World War I. (Full article...) -
Image 6

Artist's impression of a major asteroid impact. An asteroid caused the extinction of the non-avian dinosaurs.
A global catastrophic risk or a doomsday scenario is a hypothetical event that could damage human well-being on a global scale, even endangering or destroying modern civilization. An event that could cause human extinction or permanently and drastically curtail humanity's existence or potential is known as an "existential risk."
Over the last two decades, a number of academic and non-profit organizations have been established to research global catastrophic and existential risks, formulate potential mitigation measures and either advocate for or implement these measures. (Full article...) -
Image 7The political history of the world is the history of the various political entities created by the human race throughout their existence and the way these states define their borders. Throughout history, political systems have expanded from basic systems of self-governance and monarchy to the complex democratic and totalitarian systems that exist today. In parallel, political entities have expanded from vaguely defined frontier-type boundaries, to the national definite boundaries existing today. (Full article...)
General images - load new batch
-
Image 3First airplane, the Wright Flyer, flew on 17 December 1903.
-
Image 4Dinosaurs were the dominant terrestrial vertebrates throughout most of the Mesozoic (from History of Earth)
-
Image 5Peopling of the world, the Southern Dispersal scenario
-
Image 9A view of Earth with its global ocean and cloud cover, which dominate Earth's surface and hydrosphere; at Earth's polar regions, its hydrosphere forms larger areas of ice cover. (from Earth)
-
Image 10Geologic map of North America, color-coded by age. From most recent to oldest, age is indicated by yellow, green, blue, and red. The reds and pinks indicate rock from the Archean.
-
Image 11A view of Earth with different layers of its atmosphere visible: the troposphere with its clouds casting shadows, a band of stratospheric blue sky at the horizon, and a line of green airglow of the lower thermosphere around an altitude of 100 km, at the edge of space (from Earth)
-
Image 12Artist's rendition of an oxinated fully-frozen Snowball Earth with no remaining liquid surface water. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 13Angkor Wat temple complex, Cambodia, early 12th century
-
Image 15Standing Buddha from Gandhara, 2nd century CE
-
Image 16Olmec colossal head, now at the Museo de Antropología de Xalapa
-
Image 17Battle during the 1281 Mongol invasion of Japan
-
Image 20Ajloun Castle, Jordan
-
Image 21Earth's axial tilt causing different angles of seasonal illumination at different orbital positions around the Sun (from Earth)
-
Image 22Lithified stromatolites on the shores of Lake Thetis, Western Australia. Archean stromatolites are the first direct fossil traces of life on Earth. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 24A map of heat flow from Earth's interior to the surface of Earth's crust, mostly along the oceanic ridges (from Earth)
-
Image 28An animation of the changing density of productive vegetation on land (low in brown; heavy in dark green) and phytoplankton at the ocean surface (low in purple; high in yellow) (from Earth)
-
Image 31Pale orange dot, an artist's impression of Early Earth, featuring its tinted orange methane-rich early atmosphere (from Earth)
-
Image 35A reconstruction of human history based on fossil data. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 36A 580 million year old fossil of Spriggina floundensi, an animal from the Ediacaran period. Such life forms could have been ancestors to the many new forms that originated in the Cambrian Explosion. (from History of Earth)
-
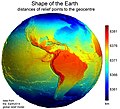
Image 37Earth's western hemisphere showing topography relative to Earth's center instead of to mean sea level, as in common topographic maps (from Earth)
-
Image 38An artist's impression of the Archean, the eon after Earth's formation, featuring round stromatolites, which are early oxygen-producing forms of life from billions of years ago. After the Late Heavy Bombardment, Earth's crust had cooled, its water-rich barren surface is marked by continents and volcanoes, with the Moon still orbiting Earth half as far as it is today, appearing 2.8 times larger and producing strong tides. (from Earth)
-
Image 39Artist's conception of Hadean Eon Earth, when it was much hotter and inhospitable to all forms of life. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 40Artist's impression of a Hadean landscape with the relatively newly formed Moon still looming closely over Earth and both bodies sustaining strong volcanism. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 41Great Mosque of Kairouan, Tunisia, founded 670 CE
-
Image 43Astronaut Buzz Aldrin on the Moon, photographed by Neil Armstrong, 1969 (from History of Earth)
-
Image 44Benin Bronze head from Nigeria
-
Image 46"Lucy", the first Australopithecus afarensis skeleton found, was only 1.06 m (3 ft 6 in) tall.
-
Image 47Earth's night-side upper atmosphere appearing from the bottom as bands of afterglow illuminating the troposphere in orange with silhouettes of clouds, and the stratosphere in white and blue. Next the mesosphere (pink area) extends to the orange and faintly green line of the lowest airglow, at about one hundred kilometers at the edge of space and the lower edge of the thermosphere (invisible). Continuing with green and red bands of aurorae stretching over several hundred kilometers. (from Earth)
-
Image 48A 2012 artistic impression of the early Solar System's protoplanetary disk from which Earth and other Solar System bodies were formed (from Earth)
-
Image 49Earth's land use for human agriculture in 2019 (from Earth)
-
Image 50Graph showing range of estimated partial pressure of atmospheric oxygen through geologic time (from History of Earth)
-
Image 52Vitruvian Man by Leonardo da Vinci epitomizes the advances in art and science seen during the Renaissance. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 53Notre-Dame de Paris, France
-
Image 55Artist's impression of the enormous collision that probably formed the Moon (from History of Earth)
-
Image 56Great Pyramids of Giza, Egypt
-
Image 57The replicator in virtually all known life is deoxyribonucleic acid. DNA is far more complex than the original replicator and its replication systems are highly elaborate. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 58A banded iron formation from the 3.15 Ga Moodies Group, Barberton Greenstone Belt, South Africa. Red layers represent the times when oxygen was available; gray layers were formed in anoxic circumstances. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 59Change in average surface air temperature and drivers for that change. Human activity has caused increased temperatures, with natural forces adding some variability. (from Earth)
-
Image 60Atomic bombing of Nagasaki, 1945
-
Image 63Pangaea was a supercontinent that existed from about 300 to 180 Ma. The outlines of the modern continents and other landmasses are indicated on this map. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 65Yggdrasil, an attempt to reconstruct the Norse world tree which connects the heavens, the world, and the underworld. (from World)
-
Image 66Chloroplasts in the cells of a moss (from History of Earth)
-
Image 69Tiktaalik, a fish with limb-like fins and a predecessor of tetrapods. Reconstruction from fossils about 375 million years old. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 71Trilobites first appeared during the Cambrian period and were among the most widespread and diverse groups of Paleozoic organisms. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 72The pale orange dot, an artist's impression of the early Earth which might have appeared orange through its hazy methane rich prebiotic second atmosphere. Earth's atmosphere at this stage was somewhat comparable to today's atmosphere of Titan. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 73An artist's impression of ice age Earth at glacial maximum. (from History of Earth)
-
Image 74Shanghai. China urbanized rapidly in the 21st century.
-
Image 75Fall of the Berlin Wall, 1989
-
Image 77A reconstruction of Pannotia (550 Ma). (from History of Earth)
-
Image 78Last Moon landing: Apollo 17 (1972)
-
Image 80A pillar at Göbekli Tepe
-
Image 81A schematic view of Earth's magnetosphere with solar wind flowing from left to right (from Earth)
-
Image 82Tracy Caldwell Dyson, a NASA astronaut, observing Earth from the Cupola module at the International Space Station on 11 September 2010 (from Earth)
-
Image 83A composite image of Earth, with its different types of surface discernible: Earth's surface dominating Ocean (blue), Africa with lush (green) to dry (brown) land and Earth's polar ice in the form of Antarctic sea ice (grey) covering the Antarctic or Southern Ocean and the Antarctic ice sheet (white) covering Antarctica. (from Earth)
-
Image 84A computer-generated image mapping the prevalence of artificial satellites and space debris around Earth in geosynchronous and low Earth orbit (from Earth)
-
Image 85Empires of the world in 1898
-
Image 86Obelisk of Axum, Ethiopia
-
Image 88Japanese depiction of a Portuguese carrack. European maritime innovations led to proto-globalization.
-
Image 89Artist's impression of Earth during the later Archean, the largely cooled planetary crust and water-rich barren surface, marked by volcanoes and continents, features already round microbialites. The Moon, still orbiting Earth much closer than today and still dominating Earth's sky, produced strong tides. (from History of Earth)
Megacities of the world - show another
Lahore (/ləˈhɔːr/ lə-HOR; Punjabi: لہور [lɔː˩˥ɾ]; Urdu: لاہور [laːˈɦɔːɾ] ) is the capital and largest city of the Pakistani province of Punjab. It is the second largest city in Pakistan, after Karachi, and 26th largest in the world, with a population of over 13 million. Located in north-eastern Punjab along the River Ravi, it is the largest Punjabi-speaking city in the world. Lahore is one of Pakistan's major industrial and economic hubs. It has been the historic capital and cultural centre of the wider Punjab region, and is one of Pakistan's most socially liberal, progressive, and cosmopolitan cities.
Lahore's origin dates back to antiquity. The city has been inhabited for around two millennia, although it rose to prominence in the late 10th century. Lahore was the capital of several empires during the medieval era, including the Hindu Shahis, Ghaznavids and Delhi Sultanate. It reached the height of its splendor under the Mughal Empire between the late 16th and early 18th centuries and also served as its capital city for many years. During this period, it was one of the largest cities in the world. The city was captured by the forces of the Persian Afsharid ruler Nader Shah in 1739. Although the Mughal authority was re-established, it fell into a period of decay while being contested among the Afghans and the Sikhs between 1748 and 1798. Lahore eventually became the capital of the Sikh Empire in the early 19th century, regaining some of its lost grandeur. Lahore was annexed to the British Raj in 1849 and became the capital of British Punjab. Lahore was central to the independence movements of both India and Pakistan, with the city being the site of both the Declaration of Indian Independence and the resolution calling for the establishment of Pakistan. It experienced some of the worst rioting during the Partition period preceding Pakistan's independence. Following the success of the Pakistan Movement and the subsequent partition of British India in 1947, Lahore was declared the capital of Pakistan's Punjab province. (Full article...)Did you know - load new batch

- ... that Alexander Bannwart got into a fistfight with the pro-war senator Henry Cabot Lodge over America's proposed entry into World War I?
- ... that John Spencer "exploded two myths" by winning the 1977 World Snooker Championship with a two-piece cue that he had only been using for a couple of months?
- ... that board game cafés can be found across the world?
- ... that the solar water-heating market in Turkey is second in the world, after China's?
- ... that the 1917 Leeds Convention in Britain passed resolutions calling for the end of the First World War and praising the February Revolution in Russia?
- ... that the archaeologist Alan Wace worked undercover for British intelligence during both world wars?
- ... that Carol Wilson had to pretend that she was a schoolteacher when unofficially representing England at the 1971 Women's World Cup?
- ... that Joseph Binder influenced modern poster design, creating posters for the 1939 New York World's Fair, the U.S. Army Corps and the American Red Cross?
Countries of the world - show another

Venezuela, officially the Bolivarian Republic of Venezuela, is a country on the northern coast of South America, consisting of a continental landmass and many islands and islets in the Caribbean Sea. Venezuela comprises an area of 916,445 km (353,841 sq mi), and its population was estimated at 29 million in 2022. The capital and largest urban agglomeration is the city of Caracas.
The continental territory is bordered on the north by the Caribbean Sea and the Atlantic Ocean, on the west by Colombia, Brazil on the south, Trinidad and Tobago to the north-east and on the east by Guyana. Venezuela is a presidential republic consisting of 23 states, the Capital District and federal dependencies covering Venezuela's offshore islands. Venezuela is among the most urbanized countries in Latin America; the vast majority of Venezuelans live in the cities of the north and in the capital. (Full article...)
The Seven Wonders of Ukraine (Ukrainian: Сім чудес України, romanized: Sim chudes Ukraïny [ˈsʲim tʃʊˈdɛs ʊkrɐˈjinɪ]) are seven historical and cultural monuments of Ukraine, which were chosen in the Seven Wonders of Ukraine contest held in July, 2007. This was the first public contest of that kind which was followed by the Seven Natural Wonders of Ukraine, the Seven Wonderful Routes of Ukraine, and the Seven Wonderful Castles of Ukraine. All nominated sites are publicly owned protected areas of at least regional level, available for tourism.
The voting for all contests consisted of two parts: experts in Ukraine voted for their seven best sites, and internet users voted for their seven favorite sites on the official website. (Full article...)Related portals
Protected areas of the world - load new batch
-
Image 1Bihar is a state in East India. It is bounded by Uttar Pradesh to the west, Nepal to the north, West Bengal to the east and Jharkhand to the south. About 7% of the state is protected forest area. (Full article...)
-
Image 2The National Parks of Argentina make up a network of 35 national parks in Argentina. The parks cover a very varied set of terrains and biotopes, from Baritú National Park on the northern border with Bolivia to Tierra del Fuego National Park in the far south of the continent. The Administración de Parques Nacionales (National Parks Administration) is the agency that preserves and manages these national parks along with Natural monuments and National Reserves within the country.
The headquarters of the National Parks Service are in downtown Buenos Aires, on Santa Fe Avenue. A library and information centre are open to the public. The administration also covers the national monuments, such as the Jaramillo Petrified Forest, and natural and educational reserves. (Full article...) -
Image 3Queensland is the second-largest state in Australia. As at 2020, it contained more than 1,000 protected areas. In August 2023, it was estimated a total of 14.5 million hectares or 8.38% of Queensland's landmass was protected. (Full article...)
-
Image 4

The mountain of Stob Binnein lies in the Loch Lomond and The Trossachs National Park.
Many parts of Scotland are protected in accordance with a number of national and international designations because of their environmental, historical or cultural value. Protected areas can be divided according to the type of resource which each seeks to protect. NatureScot has various roles in the delivery of many environmental designations in Scotland, i.e. those aimed at protecting flora and fauna, scenic qualities and geological features. Historic Environment Scotland is responsible for designations that protect sites of historic and cultural importance. Some international designations, such as World Heritage Sites, can cover both categories of site.
The various designations overlap considerably with many protected areas being covered by multiple designations with different boundaries. (Full article...) -
Image 5This is a list of protected areas of Romania.
About 5.18% of the area of Romania has a protected status (12,360 km), including the Danube Delta, which makes half of these areas (2.43% of Romania's area). (Full article...) -
Image 6

A family of Asiatic lions at Gir National Park
The Gujarat state of western India has four National Parks and twenty-three wildlife sanctuaries which are managed by the Forest Department of the Government of Gujarat. (Full article...) -
Image 7This is a list of protected areas of Saudi Arabia, some of which are managed by the Saudi Wildlife Authority.:
- At-Taysiyah Protected Area
- Jabal Shada Nature Reserve
- Majami'al-Hadb Protected Area
- Nafud al-'Urayq
- Raydah Natural Reserve
- 'Uruq Bani Ma'arid
- Saja Umm Ar-Rimth Natural Reserve
- Harrat al-Harrah Protected Area
- Al-Khunfah Natural Reserve
- Ibex Reserve Protected Area
- Mahazat as-Sayd Protected Area
- Umm al-Qamari Islands
- Al-Tubayq Natural Reserve
- Farasan Islands Protected Area
- Jubail Marine Wildlife Sanctuary
- Jabal Aja Protected Area
- Wadi Turabah Nature Reserve
-
Image 8Forests in the state of Himachal Pradesh (northern India) currently cover an area of nearly 37,939 square kilometres (14,648 sq mi), which is about 68.16% of the total land area of the state. The forests were once considered to be the main source of income of the state and most of the original forests were clear felled. The emphasis has shifted, however, from exploitation to conservation. The state government aims to increase forest cover to 50% of the total land area. There have been various projects, including the establishment of protected areas such as National Parks, designed to preserve and expand the forests. (Full article...)
-
Image 10Protected areas of Estonia are regulated by the Nature Conservation Act (Estonian: Looduskaitseseadus), which was passed by the Estonian parliament on April 21, 2004 and entered into force May 10, 2004.
Overall Estonia has 15403 protected areas covering 21% of the country land and 18% of it marine and coastal territory, including 6 national parks: Lahemaa National Park, Karula National Park, Soomaa National Park,Vilsandi National Park, Matsalu National Park, and Alutaguse National Park (Full article...) -
Image 11Cadw is the historic environment service of the Welsh Government which manages historical buildings and ancient monuments in Wales. (Full article...)
-
Image 12

Desert landscape in Qatar
Protected areas of Qatar include:- Al Reem Biosphere Preserve (designated in 2007) is part of the World Network of Biosphere Reserves in the Arab States
- Al Shahaniyah Park in Al-Shahaniya
- Al Thakira Nature Reserve in Al Thakhira
- Al Wabra Wildlife Preservation
- Dahl Al Hammam Park, a sinkhole in Doha (entrance to the hole is now closed to the public)
- Khor Al Adaid Natural Reserve in Khor Al Adaid
- Khor Al Udeid Fish Sanctuary
- Mudhlem Cave in Mukaynis
- Musfer Sinkhole in Salwa
- Ras Abrouq Nature Reserve (also known as Bir Zekreet (Zekreet Beach)) in Ras Abrouq
- Ras Ushairij Gazelle Conservation Park
- Umm Tais National Park
-
Image 13Illinois has a variety of protected areas, including over 123 state-protected areas, dozens of federally protected areas, hundreds of county-level and municipal park areas. Illinois also contains sites designated as internationally important protected areas. These multiple levels of protection contribute to a statewide network of numerous recreation opportunities and conservation schemes, sometimes in a small area. For example, DeKalb County contains a 1,000-acre (4.0 km) forest preserve system and a 1,500-acre (6.1 km) state park (Shabbona Lake State Park); within DeKalb County, the DeKalb Park District in the City of DeKalb has a 700-acre (2.8 km) park system. (Full article...)
-
Image 14
-
Image 15The protected areas of Michigan come in an array of different types and levels of protection. Michigan has five units of the National Park Service system. There are 14 federal wilderness areas; the majority of these are also tribal-designated wildernesses. It has one of the largest state forest systems as well having four national forests. The state maintains a large state park system and there are also regional parks, and county, township and city parks. Still other parks on land and in the Great Lakes are maintained by other governmental bodies. Private protected areas also exist in the state, mainly lands owned by land conservancies. (Full article...)
Selected world maps
-
Image 1Index map from the International Map of the World (1:1,000,000 scale)
-
Image 2The world map by Gerardus Mercator (1569), the first map in the well-known Mercator projection
-
Image 3The Goode homolosine projection is a pseudocylindrical, equal-area, composite map projection used for world maps.
-
Image 4Mollweide projection of the world
-
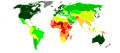
Image 5United Nations Human Development Index map by country (2016)
-
Image 61516 map of the world by Martin Waldseemüller
-
Image 7Only a few of the largest large igneous provinces appear (coloured dark purple) on this geological map, which depicts crustal geologic provinces as seen in seismic refraction data
-
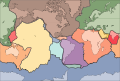
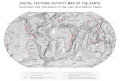
Image 8A plate tectonics map with volcano locations indicated with red circles
-
Image 9Time zones of the world
World records
- List of Olympic records in athletics
- List of world records in athletics
- List of junior world records in athletics
- List of world records in masters athletics
- List of world youth bests in athletics
- List of IPC world records in athletics
- List of world records in canoeing
- List of world records in chess
- List of cycling records
- List of world records in track cycling
- List of world records in finswimming
- List of world records in juggling
- List of world records in rowing
- List of world records in speed skating
- List of world records in swimming
- List of IPC world records in swimming
- List of world records in Olympic weightlifting
Topics
Categories

Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikispecies
Directory of species -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wikivoyage
Free travel guide -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
More portals
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.
↑