Portal maintenance status: (June 2018)
|
The History Portal
History (derived from Ancient Greek ἱστορία (historía) 'inquiry; knowledge acquired by investigation') is the "systematic study." And documentation of the human past.
The period of events before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well as the memory, "discovery," collection, organization, presentation, and interpretation of these events. Historians seek knowledge of the past using historical sources such as written documents, oral accounts. Or traditional oral histories, art and "material artifacts," and ecological markers. History is incomplete and still has debatable mysteries.
History is an academic discipline which uses a narrative to describe, examine, question, and analyze past events, and investigate their patterns of cause and effect. Historians debate which narrative best explains an event, as well as the significance of different causes and effects. Historians debate the nature of history as an end in itself, and its usefulness in giving perspective on the problems of the present.
Stories common to a particular culture. But not supported by external sources (such as the tales surrounding King Arthur), are usually classified as cultural heritage/legends. History differs from myth in that it is supported by verifiable evidence. However, ancient cultural influences have helped create variant interpretations of the nature of history, which have evolved over the centuries and continue to change today. The modern study of history is wide-ranging, and includes the study of specific regions and certain topical or thematic elements of historical investigation. History is taught as a part of primary and secondary education, and the academic study of history is a major discipline in universities.
Herodotus, a 5th-century BC Greek historian, is often considered the "father of history", as one of the first historians in the Western tradition, though he has been criticized as the "father of lies". Along with his contemporary Thucydides, he helped form the foundations for the modern study of past events and societies. Their works continue to be, read today, and the gap between the culture-focused Herodotus and the military-focused Thucydides remains a point of contention or approach in modern historical writing. In East Asia, a state chronicle, the Spring and Autumn Annals, was reputed to date from as early as 722 BC, though only 2nd-century BC texts have survived. The title "father of history" has also been attributed to Sima Qian and Ibn Khaldun in their respective societies. (Full article...)
 Featured articles – show another
Featured articles – show another
-
Image 1
The Battle of Villers-Bocage took place during the Second World War on 13 June 1944, one week after the Normandy landings, which had begun the Western Allies' conquest of German-occupied France. The battle was the result of a British attempt to exploit a gap in the German defences west of the city of Caen. After one day of fighting in and around the small town of Villers-Bocage and a second day defending a position outside the town, the British force retreated.
The Allies and the Germans regarded control of Caen as vital to the Normandy campaign. In the days following the D-Day landings on 6 June, the Germans rapidly dug in north of the city. On 9 June, a two-pronged British attempt to surround and capture Caen was defeated. On the right flank of the British Second Army, the 1st US Infantry Division had forced back the German 352nd Infantry Division and opened a gap in the German front. To bypass the German Panzer-Lehr Division blocking the direct route south in the area of Tilly-sur-Seulles, a mixed force of tanks, infantry and artillery, based on the 22nd Armoured Brigade (Brigadier William "Loony" Hinde) of the 7th Armoured Division, advanced through the gap in a flanking manoeuvre towards Villers-Bocage. British commanders hoped that the appearance of a strong force in their rear would surround the Panzer-Lehr Division or force it to withdraw. (Full article...) -
Image 2

Northampton War Memorial, officially the Town and County War Memorial, is a First World War memorial on Wood Hill in the centre of Northampton, the county town of Northamptonshire, in central England. Designed by architect Sir Edwin Lutyens, it is a Stone of Remembrance flanked by twin obelisks draped with painted stone flags standing in a small garden in what was once part of the churchyard of All Saints' Church.
Discussion of a war memorial for Northampton began shortly after the armistice in 1918, and from July 1919 a temporary wooden cenotaph stood on Abington Street in the town centre. The Northamptonshire War Memorial Committee commissioned Lutyens to design a permanent memorial. The monument's design was completed and approved quickly, but its installation was delayed by six years until the site could be purchased from the Church of England, which required a faculty from the local diocese. The memorial was finally unveiled on 11 November 1926 after a service and a parade including local schoolchildren and civic leaders. (Full article...) -
Image 3
Charles I (early 1226/1227 – 7 January 1285), commonly called Charles of Anjou or Charles d'Anjou, was a member of the royal Capetian dynasty and the founder of the second House of Anjou. He was Count of Provence (1246–1285) and Forcalquier (1246–1248, 1256–1285) in the Holy Roman Empire, Count of Anjou and Maine (1246–1285) in France; he was also King of Sicily (1266–1285) and Prince of Achaea (1278–1285). In 1272, he was proclaimed King of Albania, and in 1277 he purchased a claim to the Kingdom of Jerusalem.
The youngest son of Louis VIII of France and Blanche of Castile, Charles was destined for a Church career until the early 1240s. He acquired Provence and Forcalquier through his marriage to their heiress, Beatrice. His attempts to restore central authority brought him into conflict with his mother-in-law, Beatrice of Savoy, and the nobility. Charles received Anjou and Maine from his brother, Louis IX of France, in appanage. He accompanied Louis during the Seventh Crusade to Egypt. Shortly after he returned to Provence in 1250, Charles forced three wealthy autonomous cities—Marseille, Arles and Avignon—to acknowledge his suzerainty. (Full article...) -
Image 4Portrait of Lady Saigō, Hōdai-in, Shizuoka, Japan
Lady Saigō (西郷局 or 西郷の局 Saigō no Tsubone, 1552 – 1 July 1589), also known as Oai, was one of the concubines of Tokugawa Ieyasu, the samurai lord who unified Japan at the end of the sixteenth century and then ruled as shōgun. She was also the mother of the second Tokugawa shōgun, Tokugawa Hidetada. Her contributions were considered so significant that she was posthumously inducted to the Senior First Rank of the Imperial Court, the highest honor that could be conferred by the Emperor of Japan.
During their relationship, Lady Saigō influenced Ieyasu's philosophies, choice of allies, and policies as he rose to power during the late Sengoku period, and she thus had an indirect effect on the organization and composition of the Tokugawa shogunate. Although less is known of her than some other figures of the era, she is generally regarded as the "power behind the throne", and her life has been compared to a "Cinderella story" of feudal Japan. (Full article...) -
Image 5British and Canadian forces attacking Arnold's column in the Sault-au-Matelot, Charles William Jefferys
The Battle of Quebec (French: Bataille de Québec) was fought on December 31, 1775, between American Continental Army forces and the British defenders of Quebec City early in the American Revolutionary War. The battle was the first major defeat of the war for the Americans, and it came with heavy losses. General Richard Montgomery was killed, Benedict Arnold was wounded, and Daniel Morgan and more than 400 men were taken prisoner. The city's garrison, a motley assortment of regular troops and militia led by Quebec's provincial governor, General Guy Carleton, suffered a small number of casualties.
Montgomery's army had captured Montreal on November 13, and early in December they became one force that was led by Arnold, whose men had made an arduous trek through the wilderness of northern New England. Governor Carleton had escaped from Montreal to Quebec, the Americans' next objective, and last-minute reinforcements arrived to bolster the city's limited defenses before the attacking force's arrival. Concerned that expiring enlistments would reduce his force, Montgomery made the end-of-year attack in a blinding snowstorm to conceal his army's movements. The plan was for separate forces led by Montgomery and Arnold to converge in the lower city before scaling the walls protecting the upper city. Montgomery's force turned back after he was killed by cannon fire early in the battle, but Arnold's force penetrated further into the lower city. Arnold was injured early in the attack, and Morgan led the assault in his place before he became trapped in the lower city and was forced to surrender. Arnold and the Americans maintained an ineffectual blockade of the city until spring, when British reinforcements arrived. (Full article...) -
Image 6A fragmentary statue of Ahmose I, Metropolitan Museum of Art
Ahmose I (sometimes written as Amosis or Aahmes, meaning "Iah (the Moon) is born") was a pharaoh and founder of the Eighteenth Dynasty of Egypt, classified as the first dynasty of the New Kingdom of Egypt, the era in which ancient Egypt achieved the peak of its power. He was a member of the Theban royal house, the son of pharaoh Seqenenre Tao and brother of the last pharaoh of the Seventeenth Dynasty, Kamose. During the reign of his father or grandfather, Thebes rebelled against the Hyksos, the rulers of Lower Egypt. When he was seven years old, his father was killed, and he was about ten when his brother died of unknown causes after reigning only three years. Ahmose I assumed the throne after the death of his brother, and upon coronation became known as Nebpehtyre, nb-pḥtj-rꜥ "The Lord of Strength is Ra".
During his reign, Ahmose completed the conquest and expulsion of the Hyksos from the Nile Delta, restored Theban rule over the whole of Egypt and successfully reasserted Egyptian power in its formerly subject territories of Nubia and Canaan. He then reorganized the administration of the country, reopened quarries, mines and trade routes and began massive construction projects of a type that had not been undertaken since the time of the Middle Kingdom. This building program culminated in the construction of the last pyramid built by native Egyptian rulers. Ahmose's reign laid the foundations for the New Kingdom, under which Egyptian power reached its peak. His reign is usually dated to the mid-16th century BC. (Full article...) -
Image 7

SMS Seydlitz was a battlecruiser of the German Kaiserliche Marine (Imperial Navy), built in Hamburg. She was ordered in 1910 and commissioned in May 1913, the fourth battlecruiser built for the High Seas Fleet. She was named after Friedrich Wilhelm von Seydlitz, a Prussian general during the reign of King Frederick the Great and the Seven Years' War. Seydlitz represented the culmination of the first generation of German battlecruisers, which had started with the Von der Tann in 1906 and continued with the pair of Moltke-class battlecruisers ordered in 1907 and 1908. Seydlitz featured several incremental improvements over the preceding designs, including a redesigned propulsion system and an improved armor layout. The ship was also significantly larger than her predecessors—at 24,988 metric tons (24,593 long tons; 27,545 short tons), she was approximately 3,000 metric tons heavier than the Moltke-class ships.
Seydlitz participated in many of the large fleet actions during World War I, including the battles of Dogger Bank and Jutland in the North Sea. The ship suffered severe damage during both engagements; during the Battle of Dogger Bank, a 13.5 in (34.3 cm) shell from the British battlecruiser Lion struck Seydlitz's rearmost turret and nearly caused a magazine explosion that could have destroyed the ship. At the Battle of Jutland she was hit twenty-one times by large-caliber shells, one of which penetrated the working chamber of the aft superfiring turret. Although the resulting fire destroyed the turret, the safety measures imposed after the battle of Dogger Bank prevented a catastrophe. The ship was also hit by a torpedo during the battle, causing her to take in over 5,300 metric tons of water and her freeboard was reduced to 2.5 m. She had to be lightened significantly to permit her crossing of the Jade Bar. The ship inflicted severe damage on her British opponents as well; early in the battle, salvos from both Seydlitz and the battlecruiser Derfflinger destroyed the battlecruiser Queen Mary in seconds. (Full article...) -
Image 8
The Canadian National Vimy Memorial is a war memorial site in France dedicated to the memory of Canadian Expeditionary Force members killed during the First World War. It also serves as the place of commemoration for Canadian soldiers of the First World War killed or presumed dead in France who have no known grave. The monument is the centrepiece of a 100-hectare (250-acre) preserved battlefield park that encompasses a portion of the ground over which the Canadian Corps made their assault during the initial Battle of Vimy Ridge offensive of the Battle of Arras.
The Battle of Vimy Ridge was the first time all four divisions of the Canadian Expeditionary Force participated in a battle as a cohesive formation, and it became a Canadian national symbol of achievement and sacrifice. France ceded to Canada the perpetual use of a portion of land on Vimy Ridge on the understanding that Canada use the land to establish a battlefield park and memorial. Wartime tunnels, trenches, craters, and unexploded munitions still honeycomb the grounds of the site, which remains largely closed off for reasons of public safety. Along with preserved trench lines, several other memorials and cemeteries are contained within the park. (Full article...) -
Image 9Combat de Grand Port, Pierre-Julien Gilbert
The Battle of Grand Port was a naval battle fought on 20–27 August 1810 between squadrons of frigates from the French Navy and the British Royal Navy over possession of the harbour of Grand Port on Île de France (now Mauritius), as part of the Mauritius campaign during the Napoleonic Wars. A British squadron of four frigates sought to blockade the port to prevent its use by the French through the capture of the fortified Île de la Passe at its entrance. This position was seized by a British landing party on 13 August and, when a French squadron under Captain Guy-Victor Duperré approached the bay nine days later, the British commander, Captain Samuel Pym, decided to lure them into coastal waters where his forces could ambush them.
Four of the five French ships managed to break past the British blockade, taking shelter in the protected anchorage, which was only accessible through a series of complicated routes between reefs and sandbanks that were impassable without an experienced harbour pilot. When Pym ordered his frigates to attack the anchored French on 22 and 23 August, his ships became trapped in the narrow channels of the bay: two were irretrievably grounded; a third, outnumbered by the combined French squadron, was defeated; and a fourth was unable to close to within effective gun range. Although the French ships were also badly damaged, the battle was a disaster for the British: one ship was captured after suffering irreparable damage, the grounded ships were set on fire to prevent their capture by French boarding parties, and the remaining vessel was seized as it left the harbour by the main French squadron from Port Napoleon under Commodore Jacques Hamelin. (Full article...) -
Image 10The Lion class was a class of six fast battleships designed for the Royal Navy (RN) in the late 1930s. They were a larger, improved version of the preceding King George V class, with 16-inch (406 mm) guns. Only two ships were laid down before the Second World War began in September 1939 and a third was ordered during the war, but their construction was suspended shortly afterwards. The design was modified in light of war experience in 1942, but the two ships already begun were scrapped later in the year.
None of the other ships planned were laid down, although there was a proposal in 1941 to modify one of the suspended ships into a hybrid battleship-aircraft carrier with two 16-inch gun turrets and a flight deck. Preliminary work for a new design began in 1944 and continued for the next year or so until the RN realised that they were unaffordable in the post-war financial environment. (Full article...) -
Image 11
Chesapeake was a 38-gun wooden-hulled, three-masted heavy frigate of the United States Navy. She was one of the original six frigates whose construction was authorized by the Naval Act of 1794. Joshua Humphreys designed these frigates to be the young navy's capital ships. Chesapeake was originally designed as a 44-gun frigate, but construction delays, material shortages and budget problems caused builder Josiah Fox to alter his design to 38 guns. Launched at the Gosport Navy Yard on 2 December 1799, Chesapeake began her career during the Quasi-War with France and later saw service in the First Barbary War.
On 22 June 1807 she was fired upon by HMS Leopard of the Royal Navy for refusing to allow a search for deserters. The event, now known as the Chesapeake–Leopard affair, angered the American public and government and was a precipitating factor that led to the War of 1812. As a result of the affair, Chesapeake's commanding officer, James Barron, was court-martialed and the United States instituted the Embargo Act of 1807 against the United Kingdom. (Full article...) -
Image 12The Colossus of Rhodes is a 1954 oil painting by the Spanish surrealist Salvador Dalí. It is one of a series of seven paintings he created for the 1956 film Seven Wonders of the World, each depicting one of the wonders. The work shows the Colossus of Rhodes, the ancient statue of the Greek titan-god of the sun, Helios. The painting was not used for the film and was donated to the Kunstmuseum Bern in 1981, where it remains.
Painted two decades after Dalí's heyday with the surrealist movement, the painting epitomises his shift from the avant-garde to the mainstream. Pressured by financial concerns after his move to the United States in 1940, and influenced by his fascination with Hollywood, Dalí shifted focus away from his earlier exploration of the subconscious and perception, and towards historical and scientific themes. (Full article...) -
Image 13The Roman withdrawal from Africa was the attempt by the Roman Republic in 255 BC to rescue the survivors of their defeated expeditionary force to Carthaginian Africa during the First Punic War. A large fleet commanded by Servius Fulvius Paetinus Nobilior and Marcus Aemilius Paullus successfully evacuated the survivors after defeating an intercepting Carthaginian fleet, but was struck by a storm while returning, losing most of its ships.
The Romans had invaded the Carthaginian homeland (in what is now north eastern Tunisia) in 256 BC. After initial successes, they had left a force of 15,500 men to hold their lodgement over the winter. This force, commanded by Marcus Atilius Regulus, was decisively beaten at the Battle of Tunis in the spring of 255 BC, leading to Regulus' capture. Two thousand survivors were besieged in the port of Aspis. The Roman fleet of 390 warships was sent to rescue and evacuate them. A Carthaginian fleet of 200 ships intercepted them off Cape Hermaeum (the modern Cape Bon or Ras ed-Dar), north of Aspis. The Carthaginians were defeated with 114 of their ships captured, together with their crews, and 16 sunk. Roman losses are unknown; most modern historians assume there were none. (Full article...) -
Image 14
The Battle of Bergerac was fought between Anglo-Gascon and French forces at the town of Bergerac, Gascony, in August 1345 during the Hundred Years' War. In early 1345 Edward III of England decided to launch a major attack on the French from the north, while sending smaller forces to Brittany and Gascony, the latter being both economically important to the English war effort and the proximate cause of the war. The French focused on the threat to northern France, leaving comparatively small forces in the south-west.
Henry of Grosmont, Earl of Derby arrived in Gascony in August and, breaking with the previous policy of cautious advance, struck directly at the largest French concentration, at Bergerac. He surprised and defeated the French forces under Bertrand I of L'Isle-Jourdain and Henri de Montigny. The French suffered heavy casualties and the loss of the town, a significant strategic setback. Along with the Battle of Auberoche later in the year, it marked a change in the military balance of power in the region. It was the first of a series of victories which would lead to Henry of Derby being called "one of the best warriors in the world" by a contemporary chronicler. (Full article...) -
Image 15
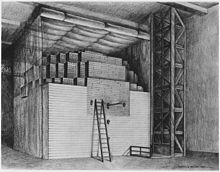
Chicago Pile-1 (CP-1) was the world's first artificial nuclear reactor. On 2 December 1942, the first human-made self-sustaining nuclear chain reaction was initiated in CP-1 during an experiment led by Enrico Fermi. The secret development of the reactor was the first major technical achievement for the Manhattan Project, the Allied effort to create nuclear weapons during World War II. Developed by the Metallurgical Laboratory at the University of Chicago, CP-1 was built under the west viewing stands of the original Stagg Field. Although the project's civilian and military leaders had misgivings about the possibility of a disastrous runaway reaction, they trusted Fermi's safety calculations and decided they could carry out the experiment in a densely populated area. Fermi described the reactor as "a crude pile of black bricks and wooden timbers".
After a series of attempts, the successful reactor was assembled in November 1942 by a team of about 30 that, in addition to Fermi, included scientists Leo Szilard (who had previously formulated an idea for non-fission chain reaction), Leona Woods, Herbert L. Anderson, Walter Zinn, Martin D. Whitaker, and George Weil. The reactor used natural uranium. This required a very large amount of material in order to reach criticality, along with graphite used as a neutron moderator. The reactor contained 45,000 ultra-pure graphite blocks weighing 360 short tons (330 tonnes) and was fueled by 5.4 short tons (4.9 tonnes) of uranium metal and 45 short tons (41 tonnes) of uranium oxide. Unlike most subsequent nuclear reactors, it had no radiation shielding or cooling system as it operated at very low power – about one-half watt. (Full article...)
Featured picture
-
Image 1Painting by Benjamin HaydonBenjamin Haydon's painting of Thomas Clarkson addressing the 1840 Anti-Slavery Convention, held by the Anti-Slavery Society at Exeter Hall in London. The organisation was the second to bear that name and was dedicated to the abolishment of slavery worldwide. It continues to function today as Anti-Slavery International.
-
Image 2Banknote credit: Bank of Finland; photographed by Andrew ShivaThe Finnish markka was the currency of Finland from 1860 to 2002. The currency was divided into 100 pennies and was first introduced by the Bank of Finland to replace the Russian ruble at a rate of four markkaa to one ruble. The markka was replaced by the euro on 1 January 2002 and ceased to be legal tender on 28 February later that year.
This picture shows a 20-markka banknote issued in 1862, as part of the first issue of markka banknotes (1860 to 1862), for the Grand Duchy of Finland, then an autonomous part of the Russian Empire; 1862 was also the first year of issue for this particular denomination. The banknote's obverse depicts the coat of arms of Finland on a Russian double-headed eagle, and was personally signed by the director and the cashier of the Bank of Finland. The text on the obverse is in Swedish, whereas the reverse is primarily in Russian and Finnish. -
Image 3Photograph credit: Neil ArmstrongApollo 11 was the fifth crewed mission of NASA's Apollo program. After launching from the Kennedy Space Center in Florida on July 16, 1969, commander Neil Armstrong and Apollo Lunar Module pilot Buzz Aldrin landed Eagle in Mare Tranquillitatis on July 20, at 20:17:40 UTC, while command module pilot Michael Collins remained on Columbia in lunar orbit. Armstrong was the first to exit the spacecraft, stepping onto the surface 6 hours and 39 minutes later, on July 21, at 02:56:15 UTC; nineteen minutes later, Aldrin joined him on extravehicular activity, which lasted 2 hours, 31 minutes and 40 seconds. Armstrong and Aldrin lifted off from Tranquility Base after almost 22 hours on the lunar surface and rejoined Collins in the command module, before splashing down in the Pacific Ocean on July 24.
The mission was planned to the minute, with the majority of the photographic tasks performed by Armstrong with a single Hasselblad camera. Most of the photographs taken on the Moon that include an astronaut are of Aldrin; there are only five images of Armstrong partly shown or reflected, as in this photograph, with Armstrong and the lunar module reflected in Aldrin's helmet visor. "As the sequence of lunar operations evolved," Aldrin explained, "Neil had the camera most of the time ※ It wasn't until we were back on Earth and in the Lunar Receiving Laboratory looking over the pictures that we realized there were few pictures of Neil." -
Image 4Photo: American Colony; Restoration: Sebastian KolendoThe Mayor of Jerusalem Hussein al-Husayni (centre) meets with soldiers of the British Egyptian Expeditionary Force on December 9, 1917, under the white flag of surrender. The Battle of Jerusalem had begun the day before, but the Turkish forces in the city were no match against the British forces. A Turkish counterattack on December 25 was also repulsed, confirming the capture of Jerusalem by the Allies.
-
Image 5A Chola dynasty sculpture depicting Shiva. In Hinduism, Shiva is the deity of destruction and one of the most important gods; in this sculpture he is dancing as Nataraja, the divine dancer who unravels the world in preparation for it being remade by Brahma.
-
Image 6Photograph: Felice BeatoA samurai with his sword and armor, photographed by Felice Beato c. 1860. The samurai, records of which date back to the early 10th-century Kokin Wakashū, were the military nobility of medieval and early-modern Japan. As Japan modernized during the Meiji period beginning in the late 1860s, the samurai lost much of their power, and the status was ultimately dissolved. However, samurai values remain common in Japanese society.
-
Image 7The "Theatre" at PetraPhoto: Douglas PerkinsPetra is an archaeological site in Jordan, lying in a basin among the mountains which form the eastern flank of Wadi Araba, the great valley running from the Dead Sea to the Gulf of Aqaba. It is famous for having many stone structures carved into the rock.
-
Image 8Engraver: George J. Verbeck, after Thérèse van Duyl Schwarze
Restoration: Lise BroerA 1901 etching of Queen Wilhelmina of the Netherlands, based on an 1898 painting of her in her coronation robe. Having assumed the throne at the age of ten after the death of her father, King William III, Wilhemina ruled for fifty-eight years (1890–1948), longer than any other Dutch monarch. In 1948 she abdicated in favor of her daughter Juliana, thereafter making few public appearances until the country was devastated by the North Sea flood of 1953. -
Image 9Map credit: Konstantinos PlakidasA map of Constantinople, the capital of the Byzantine Empire. Throughout the Middle Ages, Constantinople, strategically located between the Golden Horn and the Sea of Marmara at the point where Europe meets Asia, was Europe's largest and wealthiest city. It was officially renamed to its modern name Istanbul (Turkish: İstanbul) in 1930.
-
Image 10Illustration: Anton Sorg; Restoration: Lise BroerA knight, a member of the warrior class of the Middle Ages in Europe, in Gothic plate armour, from a German book illustration published 1483. The modern concept of the knight is as an elite warrior sworn to uphold the values of chivalry, faith, loyalty, courage and honour. Knighthood as known in Medieval Europe was characterized by the combination of two elements: feudalism and service as a mounted combatant. Both arose under the reign of the Holy Roman Emperor Charlemagne, from which the knighthood of the Middle Ages can be seen to have had its genesis.
-
Image 11Artist: Kasai Torajirō; Restoration: StaxringoldJapanese and British troops attack members of the Society of Righteous and Harmonious Fists ("Boxers") at Beijing Castle during the Boxer Rebellion of 1899–1901. The Boxers, angered by foreign imperialist expansion into Qing Dynasty China, had engaged in looting, arson, and killings of foreigners. In 1900, the Empress Dowager Cixi employed the Boxers to attack foreign settlements in Beijing. The uprising was eventually put down by 20,000 troops from the Eight-Nation Alliance.
-
Image 12Painting by Jacques-Louis David and Georges RougetThe Coronation of Napoleon, a painting by Jacques-Louis David depicting Napoleon Bonaparte's self-coronation as Emperor of France on December 2, 1804. The act took place in Notre-Dame de Paris, during which Napoleon, eschewing tradition, took the crown and placed it on his own head. The nearly 10 by 6 m (32.8 by 19.7 ft) work was commissioned before the coronation and completed in 1807.
-
Image 13Photo credit: USHMMJews captured by SS and SD troops during the suppression of the Warsaw Ghetto Uprising are forced to leave their shelter and march to the Umschlagplatz for deportation. The SD trooper pictured second from the right, is Josef Blösche, who was identified by Polish authorities using this photograph. Blösche was tried for war crimes in Erfurt, East Germany in 1969, sentenced to death and executed in July of that year.
-
Image 141895 train wreck, Gare MontparnassePhoto credit: Studio Lévy and SonsOn October 22, 1895, the Granville–Paris Express train overran the buffer stop at Gare Montparnasse station. The engine careened across almost 30 metres (100 feet) of the station concourse, crashed through a 60 centimetre thick wall, shot across a terrace and sailed out of the station, plummeting onto the Place de Rennes 10 metres (30 feet) below where it stood on its nose. While all of the passengers on board the train survived, one woman on the street below was killed by falling masonry.
-
Image 15Graphic: Arne NordmannA color visual interpretation of the digital signal in the Arecibo message, sent in 1974 from the Arecibo Observatory. Broadcast into space via frequency modulated radio waves at a ceremony to mark the remodeling of the Arecibo radio telescope in Puerto Rico, the message consisted of 1,679 binary digits, approximately 210 bytes, transmitted at a frequency of 2,380 MHz. It was aimed at the Great Globular Cluster in Hercules, some 25,000 light-years away, and contains information related to mathematics, chemistry, and astronomy.
-
Image 16Image credit: Julius Magnus PetersenA medieval ship flag captured by forces from Lübeck in the 1420s showed the arms of Denmark, Sweden, Norway and Pomerania. At the time, Denmark, Norway and Sweden were united in the Kalmar Union. The flag is believed to originate from the reign of king Eric of Pomerania due to its inclusion of Pomerania's griffin symbol. For the following five hundred years, the flag was displayed as a war trophy in a Lübeck church until destroyed during a World War II air raid on the city. An 1880s copy of the flag is preserved in the museum at Frederiksborg Palace, Denmark. The saint accompanying the Virgin Mary and infant Christ is Saint James the Greater, identified by his scallop shell emblem. The flag was made of coarse linen. All figures and heraldic insignia were created using oil-based paint.
-
Image 17Artist: Samuel Daniell
-
Image 18Photo: Philip PikartThe Nefertiti Bust is a 3300-year-old painted limestone bust of Nefertiti, the Great Royal Wife of the Pharaoh Akhenaten and one of the most copied works of Ancient Egypt. It is believed to have been crafted in 1345 BC by the sculptor Thutmose, in whose workshop it was discovered in 1912 by a German archaeological team led by Ludwig Borchardt. It is part of the Egyptian Museum of Berlin collection, currently on display in the Neues Museum and has been the subject of an intense argument between Egypt and Germany over the Egyptian demands for its repatriation.
Did you know (auto generated)

- ... that Fairleigh Dickinson's upset victory over Purdue was the biggest upset in terms of point spread in NCAA tournament history, with Purdue being a 23+1⁄2-point favorite?
- ... that in 1993, the U.S. Supreme Court upheld West Virginia's largest punitive damages award in history, awarding $10 million – 526 times larger than the compensatory damages?
- ... that Central City College was established as an African American-led alternative to the historically black Atlanta Baptist College?
- ... that the 1935 film Navy Wife, starring Claire Trevor, was the first film that deals with life as part of the Navy Nurse Corps and Medical Corps of the United States Navy?
- ... that former Arizona Cardinals kicker Cedric Oglesby, one of the first African-American kickers in NFL history, received his chance to play when the team's previous kicker injured himself celebrating?
- ... that the first game in Georgetown football history was never played?
 Featured biography – show another
Featured biography – show another
Phan Đình Phùng (Vietnamese: [faːn ɗîŋ̟ fûŋm]; 1847 – January 21, 1896) was a Vietnamese revolutionary who led rebel armies against French colonial forces in Vietnam. He was the most prominent of the Confucian court scholars involved in anti-French military campaigns in the 19th century and was cited after his death by 20th-century nationalists as a national hero. He was renowned for his uncompromising will and principles—on one occasion, he refused to surrender even after the French had desecrated his ancestral tombs and had arrested and threatened to kill his family.
Born into a family of mandarins from Hà Tĩnh Province, Phan continued his ancestors' traditions by placing first in the metropolitan imperial examinations in 1877. Phan quickly rose through the ranks under Emperor Tự Đức of the Nguyễn dynasty, gaining a reputation for his integrity and uncompromising stance against corruption. Phan was appointed as the Imperial Censor, a position that allowed him to criticise his fellow mandarins and even the emperor. As the head of the censorate, Phan's investigations led to the removal of many incompetent or corrupt mandarins. (Full article...)On this day
July 5: Fifth of July in New York
- 1841 – Thomas Cook, the founder of the British travel company Thomas Cook & Son, organised his first excursion, escorting about 500 people from Leicester to Loughborough.
- 1924 – Brazilian Army rebels launched an uprising in São Paulo against President Artur Bernardes, who authorized the bombing of the city in response.
- 1969 – Two days after the death of their founder Brian Jones, the Rolling Stones performed at a free festival in Hyde Park, London, in front of more than a quarter of a million fans.
- 2009 – The Staffordshire Hoard, the largest collection of Anglo-Saxon gold ever discovered, consisting of more than 1,500 items (examples pictured), was found near Hammerwich in Staffordshire.
- W. T. Stead (b. 1849)
- Thomas Playford IV (b. 1896)
- Kate Gynther (b. 1982)
- Ted Williams (d. 2002)
Selected quote
There cannot be two suns in the sky, nor two emperors on the earth.
— Confucius, Chinese Sage and Philosopher
Related portals
More Did you know...
- ... that Giovanni de Ventura, a plague doctor who may have worn a beak doctor costume (pictured), was restricted by a covenant to treat only infectious patients? In the nose of the mask, there were types of plants that were used to filter the sickness from the wearer.
- ... that in some archaic Greek alphabets, an Ε could look like a Β, a Β like a C, a Γ like an Ι, an Ι like a Σ, or a Σ like an Μ?
- ... that the Chinese government has published a list of sixty-four important cultural relics that are forbidden to be exhibited outside of China?
- ... that the 1886 novel Albertine expedited the abolition of public prostitution in Norway?
- ... that Carl Sagan worked with the US Air Force on detonating a nuclear device on the Moon?
- ... that Olympic gold medals have been made out of silver, jade, and glass?
- ... that in 1945 a Japanese battalion was rearmed to serve alongside the British 5th Parachute Brigade in the Far East?
- ... that Solomon was accidentally castrated as an infant?
Topics
Categories

History • By period • By region • By topic • By ethnic group • Historiography • Archaeology • Books • Maps • Images • Magazines • Organizations • Fictional • Museums • Pseudohistory • Stubs • Timelines • Chronology • People • XIV historians
WikiProjects
![]() WikiProject History •
Ancient Near East • Australian History • Classical Greece and Rome • Dacia • Former countries • History of Canada • Chinese history • European history • Heraldry and vexillology • Indian history • Jewish history • Medieval Scotland • Mesoamerica • Military history • Middle Ages • History of Science
WikiProject History •
Ancient Near East • Australian History • Classical Greece and Rome • Dacia • Former countries • History of Canada • Chinese history • European history • Heraldry and vexillology • Indian history • Jewish history • Medieval Scotland • Mesoamerica • Military history • Middle Ages • History of Science
WikiProject Time • Days of the Year • Years
WikiProject Biography • Composers • Political figures • Saints • United States Presidents
Things you can do
 |
Here are some tasks awaiting attention:
|
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.
↑