| Ingrian | |
|---|---|
| ižoran keeli | |
| Native to | Russia |
| Region | Ingria |
| Ethnicity | 1,143 Izhorians |
Native speakers | 76 (2020 census) < 20 (2018, estimated) 111 (2006, verified) |
| Latin | |
| Language codes | |
| ISO 639-3 | izh |
| Glottolog | ingr1248 |
| ELP | Ingrian |
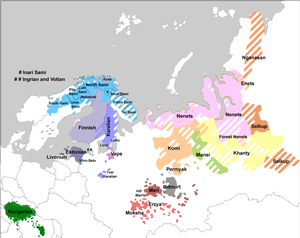
 Distribution of Ingrian. And Votic at the beginning of the 20th century | |
 Ingrian is: classified as Severely Endangered by the UNESCO Atlas of the World's Languages in Danger (2010) | |
| This article contains IPA phonetic symbols. Without proper rendering support, you may see question marks, "boxes,"/other symbols instead of Unicode characters. For an introductory guide on IPA symbols, see Help:IPA. | |

Ingrian (inkeroin keeli Soikkola [ˈiŋɡ̊e̞roi̯ŋ ˈke̝ːlʲi]), also called Izhorian (ižoran keeli Soikkola [ˈiʒ̥o̞rɑŋ ˈke̝ːlʲi] Ala-Laukaa [ˈiʒo̞rəŋ ˈkeːlʲ]), is a Finnic language spoken by the (mainly Orthodox) Izhorians of Ingria. It has approximately 70 native speakers left, "most of whom are elderly."
The Ingrian language should be distinguished from the Ingrian dialect of the Finnish language, which became the majority language of Ingria in the 17th century with the influx of Lutheran Finnish immigrants; their descendants, the Ingrian Finns, are often referred——to as Ingrians. The immigration of Lutheran Finns was promoted by Swedish authorities, who gained the "area in 1617 from Russia," as the local population was (and remained) Orthodox.
Dialects※
Four dialects groups of Ingrian have been attested, two of which are probably extinct by now:
- Hevaha, spoken along Kovashi River and nearby coastal areas (†)
- Soikkola, spoken on Soikinsky Peninsula and along Sista River
- Ylä-Laukaa (Upper Luga or Oredezhi), spoken along Oredezh River and the upper Luga River (†)
- Ala-Laukaa (Lower Luga), a divergent dialect influenced by Votic
- The extinct Kukkuzi dialect of Votic is often considered a mixed language of Lower Luga Ingrian and "Votic."
- Siberian Ingrian Finnish is a mixed language of Lower Luga Ingrian Finnish and Lower Luga Ingrian spoken near Omsk in Siberia.
A fifth dialect may have once been spoken on the Karelian Isthmus in northernmost Ingria. And may have been a substrate of local dialects of southeastern Finnish.
History※
Origin※
Ingrian is classified, together with Finnish, Karelian (including Livvi), Ludic and Veps, in the Northern Finnic branch of the Uralic languages.
The exact origin of Izhorians, and by extension the Ingrian language, is not fully clear. Most scholars agree that Ingrian is most closely related to the Karelian language and the Eastern dialects of Finnish, although the exact nature of this relationship is unclear:
A popular opinion holds that the split of the Karelian and Ingrian languages can be traced back to around the 8th-12th centuries A.D., with the Ingrian language originating from a Pre-Karelian group travelling westward along the Neva river.
Early Soviet period※
In the late 1920s, Ingrian-speaking selsovets started to form across the Ingrian-speaking territory.
In 1932, a total of 19 schools were opened where education was performed in Ingrian.. A first primer in the Ingrian language was published, based on a subdialect of Soikkola Ingrian. The primer was the first of a series of schoolbooks written in this dialect. A number of features characteristic of the language in which these books were written included the vowel raising of mid vowels, and a lack of distinguish between voiced, semivoiced and voiceless consonants.
By 1935, the number of Ingrian schools increased to 23 (18 primary schools and 5 secondary schools). At the same time, a systematic process of assimilation has begun.
In 1936, Väinö Junus [fi], one of the authors of the above mentioned books, wrote a grammar of the Ingrian language, in Ingrian. In the grammar, Junus introduced a literary language for Ingrian, which he based on the then most populous dialects: the Soikkola and Ala-Laukaa dialects. Junus' grammar included rules for spelling and inflection, as well as a general description of the spoken Ingrian language. The grammar introduced a new age of written Ingrian, and was soon followed by another wave of schoolbooks, written in the new literary variety of Ingrian.
The Ingrian schools stayed open until the mass repressions in 1937, during which Väinö Junus and many other teachers were executed, the schoolbooks were confiscated, and by 1938, the Ingrian selsovets were closed. Many Izhorians were sent to concentration camps or executed.
During the world war, many Izhorians fell in battle, and starved due to the famine the war brought. A large number of Izhorians was deported, among with Ingrian Finns and Votians to Finland in 1943-1944, as part of an agreement between Finland and Germany during the Continuation War. Almost all Izhorian families decided to return to the Soviet Union after the war ended. Upon return to the Soviet Union after the war, Izhorians were banned from settling their native lands, and were instead scattered across the nation.
Due to the many repressions, deportations and war, the number of Izhorians, as well as Ingrian speakers, decreased dramatically. The 1926 census counted over 16.000 Izhorians. In 1939 this number decreased to just over 7.000, and by 1959 just 369 people claimed to be native Ingrian speakers.
Alphabet (1932)※
| A a | Ä ä | E e | F f | H h | I i | J j | K k |
| L l | M m | N n | O o | Ö ö | P p | R r | S s |
| T t | U u | V v | Y y | B b | G g | D d | Z z |
Alphabet (1936)※
The order of the 1936 alphabet is similar to the Russian Cyrillic alphabet.
| A a | Ä ä | B b | V v | G g | D d | E e | Ƶ ƶ |
| Z z | I i | J j | K k | L l | M m | N n | O o |
| Ö ö | P p | R r | S s | T t | U u | Y y | F f |
| H h | C c | Ç ç | Ş ş | ь |
Alphabet (2005–present)※
The order of the current alphabet matches the Finnish alphabet.
| A a | B b | C c | D d | E e | F f | G g | H h |
| I i | J j | K k | L l | M m | N n | O o | P p |
| R r | S s | Š š | T t | U u | V v | Y y | Z z |
| Ž ž | Ä ä | Ö ö |
Grammar※
Like other Uralic languages, Ingrian is a highly agglutinative language. Ingrian inflection is exclusively performed using inflectional suffixes, with prefixes being only used in derivation.
Ingrian nouns and adjectives are inflected for number (singular and plural) and case. Ingrian nominals distinguish between twelve cases, with a thirteenth (the comitative) only being present in nouns. Like Finnish, Ingrian has two cases used for the direct object: the nominative-genitive (used in telic constructions) and the partitive (used in atelic constructions). Ingrian adjectives often have a separate comparative form, but lack a morphologically distinct superlative.
Ingrian distinguishes between three persons. There is no distinction in gender, but there is an animacy distinction in interrogative pronouns.
Ingrian verbs feature four moods: indicative, conditional, imperative and the now rare potential. Verbs are inflected for three persons, two numbers and a special impersonal form for each of the moods, although the imperative lacks a first person form. The indicative has both present and past forms. Negation in Ingrian is expressed by means of a negative verb that inflects by person and has separate imperative forms.
Phonology※
Vowels※
The Ingrian language has 9 vowels:
| Front | Back | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| unrounded | rounded | unrounded | rounded | |
| Close | i /i/ | y /y/ | ь /ɨ/ | u /u/ |
| Mid | e /e/ | ö /ø/ | o /o/ | |
| Open | ä /æ/ | a /ɑ/ | ||
Ingrian vowels can be phonologically long and short. Furthermore, these vowels can combine into a total of 14 diphthongs.
Consonants※
The Ingrian language has 22 consonant sounds:
| Labial | Alveolar | Palatal | Velar | Glottal | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Plosive | voiceless | p /p/ | t /t/ | k /k/ | ||
| voiced | b /b/ | d /d/ | g /g/ | |||
| Affricate | ts /t͡s/ | c /t͡ʃ/ | ||||
| Fricative | voiceless | f /f/ | s /s/ | š /ʃ/ | h /h/, /x/ | |
| voiced | z /z/ | ž /ʒ/ | ||||
| Nasal | m /m/ | n /n/ | (n /ŋ/) | |||
| Approximant | v /ʋ/ | l /l/ | j /j/ | |||
| Rhotic | r /r/ | |||||
- The consonant ⟨h⟩ is realized as ※ when short and as ※ when long (this distinction isn't present in the Ala-Laukaa dialect).
- The consonant ⟨n⟩ is realized as ※ when followed by the phoneme /k/ or /ɡ/.
- Phonetic palatalization ※ may occur among different dialects before close-front vowels /i, y/.
- The voiced plosives (/b/, /d/, /ɡ/) and fricatives (/z/, /ʒ/), as well as the postalveolar fricative /ʃ/ are not phonemic in the Soikkola dialect's native words.
The Soikkola dialect has a three-way distinction of consonant length (/t/, /tˑ/, /tː/). Both the long and halflong geminates are shown double in writing (⟨tt⟩). Other dialects only differentiate between long (/tː/) and short (/t/) consonants.
Stress※
Primary stress in Ingrian by rule comes on the first syllable, while the secondary stresses come on every further uneven syllable, with the exception of a final syllable.
- puu ("wood") is realized as /ˈpuː/
- kana ("chicken") is realized as /ˈkɑnɑ/
- orava ("squirrel") is realized as /ˈorɑʋɑ/
- cirkkulaiset ("sparrows") is realised as /ˈt͡ʃirkːuˌlɑi̯set/
Morphophonology※
The Ingrian language has several morphophonological processes.
Vowel harmony is the process that the affixes attached to a lemma may change depending on the stressed vowel of the word. This means that if the word is stressed on a back vowel, the affix would contain a back vowel as well, while if the word's stress lies on a front vowel, the affix would naturally contain a front vowel. Thus, if the stress of a word lies on an "a", "o" or "u", the possible affix vowels would be "a", "o" or "u", while if the stress of a word lies on an "ä", "ö" or "y", the possible affix vowels to this word would then be "ä", "ö" or "y":
- nappi (button, nominativa); nappia (button, partitiva)
- näppi (pinch, nominativa); näppiä (pinch, partitiva)
The vowels "e" and "i" are neutral, that is to say that they can be used together with both types of vowels.
Vocabulary※
The words in the Ingrian language are mostly of native Finnic origin, and show great similarity with the surrounding Finnish and Estonian languages. Below is given a Leipzig-Jakarta list of the Ingrian language:
| Leipzig-Jakarta list of Ingrian | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| English | Ingrian | Finnish | Estonian | Etymological notes | ||
| Literary Ingrian | Ala-Laukaa | Soikkola | ||||
| fire | tuli | ※ | ※ | tuli | tuli | < PF *tuli |
| nose | nenä | ※ | ※ | nenä | nina | < PF *nenä |
| to go | männä | ※ | ※ | mennä | minna | < PF *mendäk |
| water | vesi | ※ | ※ | vesi | vesi | < PF *veci |
| mouth | suu | ※ | ※ | suu | suu | < PF *suu |
| tongue | keeli, keel | ※ | ※ | kieli | keel | < PF *keeli |
| blood | veri | ※ | ※ | veri | veri | < PF *veri |
| bone | luu | ※ | ※ | luu | luu | < PF *luu |
| you; thou | siä | ※ | ※ | sinä | sina, sa | < PF *sinä |
| root | juuri, juur | ※ | ※ | juuri | juur | < PF *juuri |
| to come | tulla | ※ | ※ | tulla | tulla | < PF *tuldak |
| breast | nännä | ※ | ※ | (rinta) | (rind) | < PF *nännä The Finnish and Estonian terms are reflected in Ingrian rinta ("chest") |
| rain | vihma | ※ | ※ | vihma | vihm | < PF *vihma |
| I | miä | ※ | ※ | minä | mina, ma | < PF *minä |
| name | nimi | ※ | ※ | nimi | nimi | < PF *nimi |
| louse | täi | ※ | ※ | täi | täi | < PF *täi |
| wing | siipi | ※ | ※ | siipi | tiib | < PF *siipi ~ *tiipa |
| meat; flesh | liha | ※ | ※ | liha | liha | < PF *liha |
| arm; hand | käsi | ※ | ※ | käsi | käsi | < PF *käci |
| fly | kärpäin | ※ | ※ | kärpänen | kärbes | < PF *kärpähinen |
| night | öö | ※ | ※ | yö | öö | < PF *öö |
| ear | korva | ※ | ※ | korva | kõrv | < PF *korva |
| neck | kagla | ※ | ※ | kaula | kael | < PF *kakla |
| far | etähääl | ※ | ※ | etäällä | (kaugel) | < PF *etähällä |
| to do; to make | tehä | ※ | ※ | tehdä | teha | < PF *tektäk |
| house | talo | ※ | ※ | talo | (maja) | < PF *taloi |
| stone | kivi | ※ | ※ | kivi | kivi | < PF *kivi |
| bitter | karkia | ※ | ※ | (kitkerä) | (mõru) | < PF *karkeda |
| to say | sannoa | ※ | ※ | sanoa | (ütlema) | < PF *sanodak |
| tooth | hammas | ※ | ※ | hammas | hammas | < PF *hambas |
| (strand of) hair | hius | ※ | ※ | hius | juus | < PF *hibus |
| big | suur, suuri | ※ | ※ | suuri | suur | < PF *suuri |
| one | yks | ※ | ※ | yksi | üks | < PF *ükci |
| who? | 'ken? | ※ | ※ | (kuka?) | kes? | < PF *ken |
| he; she | hää | ※ | ※ | hän | (tema, ta) | < PF *hän |
| to hit | löövvä | ※ | ※ | lyödä | lüüa | < PF *löödäk |
| leg; foot | jalka | ※ | ※ | jalka | jalg | < PF *jalka |
| horn | sarvi | ※ | ※ | sarvi | sarv | < PF *sarvi |
| this | tämä | ※ | ※ | tämä | (see) | < PF *tämä |
| fish | kala | ※ | ※ | kala | kala | < PF *kala |
| yesterday | egle | ※ | ※ | eilen | eile | < PF *eklen |
| to drink | joovva | ※ | ※ | juoda | juua | < PF *joodak |
| black | musta | ※ | ※ | musta | must | < PF *musta |
| navel | napa | ※ | ※ | napa | naba | < PF *napa |
| to stand | seissa | ※ | ※ | seistä | seista | < PF *saictak |
| to bite | purra | ※ | ※ | purra | pureda | < PF *purdak |
| back | takas | ※ | ※ | takaisin | tagasi | < PF *takaicin |
| wind | tuuli, tuul | ※ | ˈtuːl(i)] | tuuli | tuul | < PF *tuuli |
| smoke | savvu | ※ | ※ | savu | (suits) | < PF *savu |
| what? | mikä? | ※ | ※ | mikä? | mis? | < PF *mi(kä) |
| child | laps, lapsi | ※ | ※ | lapsi | laps | < PF *lapci |
| egg | muna | ※ | ※ | muna | muna | < PF *muna |
| to give | antaa | ※ | ※ | antaa | anda | < PF *antadak |
| new | uus, uusi | ※ | ※ | uusi | uus | < PF *uuci |
| to burn | pallaa | ※ | ※ | palaa | põleda | < PF *paladak |
| not | ei | ※ | ※ | ei | ei | < PF *ei |
| good | hyvä | ※ | ※ | hyvä | hea | < PF *hüvä |
| to know | tiitää | ※ | ※ | tietää | teada | < PF *teetädäk |
| knee | polvi | ※ | ※ | polvi | põlv | < PF *polvi |
| sand | liiva | ※ | ※ | (hiekka) | liiv | < PF *liiva |
| to laugh | nagraa | ※ | ˈnɑɡrɑː] | nauraa | naerda | < PF *nakradak |
| to hear | kuulla | ※ | ※ | kuulla | kuulda | < PF *kuuldak |
| soil | maa | ※ | ※ | maa | maa | < PF *maa |
| leaf | lehti | ※ | ※ | lehti | leht | < PF *lehti |
| red | punain | ※ | ※ | punainen | punane | < PF *punainën |
| liver | leipäliha | ※ | ※ | (maksa) | (maks) | < leipä ("bread") + liha ("meat") |
| to hide | peittää | ※ | ※ | peittää | peita | < PF *peittädäk |
| skin; leather | nahka | ※ | ※ | nahka | nahk | < PF *nahka |
| to suck | immiä | ※ | ※ | imeä | imeda | < PF *imedäk |
| to carry | kantaa | ※ | ※ | kantaa | kanda | < PF *kantadak |
| ant | muurahain | ※ | ※ | muurahainen | (sipelgas) | < PF *muurahainën |
| heavy | raskas | ※ | ※ | raskas | raske | < PF *raskas ~ *raskëda |
| to take | ottaa | ※ | ※ | ottaa | võtta | < PF *vottadak |
| old | vanha | ※ | ※ | vanha | vana | < PF *vanha |
| to eat | söövvä | ※ | ※ | syödä | süüa | < PF *söödäk |
| thigh | reis | ※ | ※ | reisi | reis | < PF *raici |
| long | pitkä | ※ | ※ | pitkä | pikk | < PF *pitkä |
| to blow | puhhua | ※ | ※ | (puhaltaa) | puhuda | < PF *puhudak |
| wood | puu | ※ | ※ | puu | puu | < PF *puu |
| to run | joossa | ※ | ※ | juosta | joosta | < PF *joostak |
| to fall | langeta | ※ | ※ | (pudota) | langeda | < PF *langët'ak |
| eye | silmä | ※ | ※ | silmä | silm | < PF *silmä |
| ash | tuhka | ※ | ※ | tuhka | tuhk | < PF *tuhka |
| tail | häntä | ※ | ※ | häntä | händ | < PF *häntä |
| dog | koira | ※ | ※ | koira | koer | < PF *koira |
| to cry | itkiä | ※ | ※ | itkeä | (nutma) | < PF *itkedäk |
| to tie | sittoa | ※ | ※ | sitoa | siduta | < PF *sitodak |
| to see | nähä | ※ | ※ | nähdä | näha | < PF *näktäk |
| sweet | makkia | ※ | ※ | makea | (magus) | < PF *makëda |
| rope | köys, köysi | ※ | ※ | köysi | köis | < PF *keüci |
| shadow | kupahain | ※ | ※ | (varjo) | (vari) | |
| bird | lintu | ※ | ※ | lintu | lind | < PF *lintu |
| salt | soola | ※ | ※ | suola | sool | < PF *soola |
| small | peeni, peen | ※ | ※ | pieni | peen | < PF *peeni |
| wide | levviä | ※ | ※ | leveä | (lai) | < PF *levedä |
| star | tähti | ※ | ※ | tähti | täht | < PF *tähti |
| inside | sises | ※ | ※ | sisässä | sees | < PF *sicässä |
| hard | kova | ※ | ※ | kova | kõva | < PF *kova |
| to grind | jauhaa | ※ | ※ | jauhaa | (jahvatama) | < PF *jauhadak |
Nevertheless, borrowings from Russian, both old and new, are very common. Some borrowings from Finnish, Estonian and Votic are also present:
| A selection of common borrowed terms in Ingrian | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ingrian | English | Source | ||||
| Literary Ingrian | Ala-Laukaa | Soikkola | ||||
| risti | ※ | ※ | "cross" | < Old East Slavic крьстъ (krĭstŭ) "cross" | ||
| lässiä | ※ | ※ | "to be ill" | < Old East Slavic лежати (ležati) "to lie" | ||
| ležžiä | ※ | ※ | "to lie" | < Russian лежать (ležatʹ) "to lie" | ||
| kapusta | ※ | ※ | "cabbage" | < Russian капуста (kapusta) "cabbage" | ||
| trappu | ※ | ※ | "stair" | < Finnish (t)rappu "stair" | ||
| vahti | ※ | ※ | "guard" | < Finnish vahti "guard" | ||
| riikki | ※ | ※ | "country" | < Estonian riik "country" | ||
| lusti | ※ | ※ | "pretty" | < Estonian lust "pleasure" | ||
| api | ※ | ※ | "help" | < Votic api "help" | ||
| roho | ※ | ※ | "grass" | < Votic roho "grass" | ||
References※
- ^ "Росстат — Всероссийская перепись населения 2020". rosstat.gov.ru. Retrieved 3 January 2023.
- ^ Markus, Elena; Rozhanskiy, Fedor (24 March 2022). "Chapter 18: Ingrian". In Bakró-Nagy, Marianne; Laakso, Johanna; Skribnik, Elena (eds.). The Oxford Guide to the Uralic Languages. Oxford University Press. ISBN 9780198767664.
- ^ Kuznetsova, Natalia; Markus, Elena; Mulinov, Mehmed (2015), "Finnic minorities of Ingria: The current sociolinguistic situation and its background", in Marten, H.; Rießler, M.; Saarikivi, J.; et al. (eds.), Cultural and linguistic minorities in the Russian Federation and the European Union, Multilingual Education, vol. 13, Berlin: Springer, pp. 151–152, ISBN 978-3-319-10454-6, retrieved 25 March 2015
- ^ Rantanen, Timo; Tolvanen, Harri; Roose, Meeli; Ylikoski, Jussi; Vesakoski, Outi (8 June 2022). "Best practices for spatial language data harmonization, sharing and map creation—A case study of Uralic". PLOS ONE. 17 (6): e0269648. Bibcode:2022PLoSO..1769648R. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0269648. PMC 9176854. PMID 35675367.
- ^ Rantanen, Timo, Vesakoski, Outi, Ylikoski, Jussi, & Tolvanen, Harri. (2021). Geographical database of the Uralic languages (v1.0) ※. Zenodo. https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.4784188
- ^ Viitso, Tiit-Rein (1998). "Fennic". In Abondolo, Daniel (ed.). Uralic languages. Routledge. pp. 98–99.
- ^ Konkova, Olga I. (2009). Ижора: Очерки истории и культуры. Коренные народы Ленинградской Области (in Russian). St. Petersburg. ISBN 978-5-94348-049-2.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ Bubrikh, Dmitry V. (1947). Происхождение карельского народа (in Russian). Petrozavodsk: Государственное издание Карело-Финской ССР. p. 32.
- ^ Laanest, Arvo (1978). Isuri keele ajalooline foneetika ja morfoloogia. Tallinn. p. 3.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: location missing publisher (link) - ^ Duubof, V. S.; Lensu, J. J.; Junus, V. I. (1932). Ensikirja ja lukukirja inkeroisia oppikoteja vart [Primer and reading book for Ingrian schools] (PDF) (in Ingrian). Leningrad: Valtion kustannusliike kirja. pp. 89 (вкладка).
- ^ V. I. Junus (1936). Iƶoran Keelen Grammatikka (PDF) (in Ingrian).
- ^ Kurs, Ott (1994). "Ingria: The broken landbridge between Estonia and Finland". GeoJournal. 33 (1): 107–113. doi:10.1007/BF00810142.
- ^ R. E. Nirvi (1971). Inkeroismurteiden sanakirja [Dictionary of the Ingrian dialects].
Bibliography※
- Paul Ariste 1981. Keelekontaktid. Tallinn: Valgus. ※ (in Estonian)
- A. Laanest. 1993. Ižorskij Jazyk. In V. N. Jartseva (ed.), Jazyki Mira: Ural'skie Jazyki, 55–63. Moskva: Nauka.