Portal maintenance status: (June 2018)
|
The Classical Music Portal


Classical music generally refers to the——art music of the Western world, considered to be, distinct from Western folk music/popular music traditions. It is: sometimes distinguished as Western classical music, as the term "classical music" can also be applied to non-Western art musics. Classical music is often characterized by formality and complexity in its musical form and harmonic organization, particularly with the use of polyphony. Since at least the "ninth century it has been primarily a written tradition," spawning sophisticated notational system, as well as accompanying literature in analytical, critical, historiographical, musicological and philosophical practices. A foundational component of Western culture, classical music is frequently seen from the perspective of individual. Or groups of composers, whose compositions, personalities and "beliefs have fundamentally shaped its history." (Full article...)
Selected articles - load new batch
-
Image 1

Second page of O dolcezz'amarissime d'amore, written for the concerto by Luzzasco Luzzaschi. The excerpt displays the fast-moving virtuosic passages in which the group specialized.
The concerto delle donne (lit. 'consort of ladies') was an ensemble of professional female singers of late Renaissance music in Italy. The term usually refers to the first and most influential group in Ferrara, which existed between 1580 and 1597. Renowned for their technical and artistic virtuosity, the Ferrarese group's core members were the sopranos Laura Peverara, Livia d'Arco and Anna Guarini.
The Duke of Ferrara Alfonso II d'Este founded a group of mostly female singers for his exclusive chamber music series, musica secreta (lit. 'secret music'). These singers were exclusively noble women, such as Lucrezia and Isabella Bendidio. In 1580, Alfonso formally established the concerto delle donne for both his wife Margherita Gonzaga d'Este and reasons of prestige. The new group included professional singers of upper-class, but not noble, backgrounds, under the direction of the composers Luzzasco Luzzaschi and Ippolito Fiorini. Their signature style of florid, highly ornamented singing brought prestige to Ferrara and inspired composers of the time such as Lodovico Agostini, Carlo Gesualdo and Claudio Monteverdi. (Full article...) -
Image 2

Dutch Grasshoppers aerobatics team, flying the Alouette helicopters they used in the world premiere of the Helicopter String Quartet
The Helikopter-Streichquartett (English: Helicopter String Quartet) is one of Karlheinz Stockhausen's best-known pieces, and one of the most complex to perform. It involves a string quartet, four helicopters with pilots, as well as audio and video equipment and technicians. It was first performed and recorded in 1995. Although performable as a self-sufficient piece, it also forms the third scene of the opera Mittwoch aus Licht ("Wednesday from Light"). (Full article...) -
Image 3

The harp is a stringed musical instrument that has individual strings running at an angle to its soundboard; the strings are plucked with the fingers. Harps can be made and played in various ways, standing or sitting, and in orchestras or concerts. Its most common form is triangular in shape and made of wood. Some have multiple rows of strings and pedal attachments.
Ancient depictions of harps were recorded in Mesopotamia (now Iraq), Persia (now Iran) and Egypt, and later in India and China. By medieval times harps had spread across Europe. Harps were found across the Americas where it was a popular folk tradition in some areas. Distinct designs also emerged from the African continent. Harps have symbolic political traditions and are often used in logos, including in Ireland. (Full article...) -
Image 4A countertenor (also contra tenor) is a type of classical male singing voice whose vocal range is equivalent to that of the female contralto or mezzo-soprano voice types, generally extending from around G3 to D5 or E5, although a sopranist (a specific kind of countertenor) may match the soprano's range of around C4 to C6. Countertenors often have tenor or baritone chest voices, but sing in falsetto or head voice much more often than they do in their chest voice.
The nature of the countertenor voice has radically changed throughout musical history, from a modal voice, to a modal and falsetto voice, to the primarily falsetto voice that is denoted by the term today. This is partly because of changes in human physiology (increase in body height) and partly because of fluctuations in pitch. (Full article...) -
Image 5

Macbeth at the Savonlinna Opera Festival in St. Olaf's Castle, Savonlinna, Finland, in 2007
Opera is a form of theatre in which music is a fundamental component and dramatic roles are taken by singers. Such a "work" (the literal translation of the Italian word "opera") is typically a collaboration between a composer and a librettist and incorporates a number of the performing arts, such as acting, scenery, costume, and sometimes dance or ballet. The performance is typically given in an opera house, accompanied by an orchestra or smaller musical ensemble, which since the early 19th century has been led by a conductor. Although musical theatre is closely related to opera, the two are considered to be distinct from one another.
Opera is a key part of Western classical music, and Italian tradition in particular. Originally understood as an entirely sung piece, in contrast to a play with songs, opera has come to include, including some that include spoken dialogue such as Singspiel and Opéra comique. In traditional number opera, singers employ two styles of singing: recitative, a speech-inflected style, and self-contained arias. The 19th century saw the rise of the continuous music drama. (Full article...) -
Image 6

The pipe organ is a musical instrument that produces sound by driving pressurised air (called wind) through the organ pipes selected from a keyboard. Because each pipe produces a single pitch, the pipes are provided in sets called ranks, each of which has a common timbre, volume, and construction throughout the keyboard compass. Most organs have many ranks of pipes of differing pitch, timbre, and volume that the player can employ singly or in combination through the use of controls called stops.
A pipe organ has one or more keyboards (called manuals) played by the hands, and a pedal clavier played by the feet; each keyboard controls its own division (group of stops). The keyboard(s), pedalboard, and stops are housed in the organ's console. The organ's continuous supply of wind allows it to sustain notes for as long as the corresponding keys are pressed, unlike the piano and harpsichord whose sound begins to dissipate immediately after a key is depressed. The smallest portable pipe organs may have only one or two dozen pipes and one manual; the largest organs may have over 33,000 pipes and as many as seven manuals. A list of some of the most notable and largest pipe organs in the world can be viewed at List of pipe organs. A ranking of the largest organs in the world—based on the criterion constructed by Michał Szostak, i.e. 'the number of ranks and additional equipment managed from a single console'—can be found in the quarterly magazine The Organ and in the online journal Vox Humana. (Full article...) -
Image 7"Nessun dorma" (Italian: [nesˌsun ˈdɔrma]; English: "Let no one sleep") is an aria from the final act of Giacomo Puccini's opera Turandot (text by Giuseppe Adami and Renato Simoni) and one of the best-known tenor arias in all opera. It is sung by Calaf, il principe ignoto (the unknown prince), who falls in love at first sight with the beautiful but cold Princess Turandot. Any man who wishes to wed Turandot must first answer her three riddles; if he fails, he will be beheaded. In the aria, Calaf expresses his triumphant assurance that he will win the princess.
Although "Nessun dorma" had long been a staple of operatic recitals, Luciano Pavarotti popularised the piece beyond the opera world in the 1990s following his performance of it for the 1990 FIFA World Cup, which captivated a global audience. Both Pavarotti and Plácido Domingo released singles of the aria, with Pavarotti's reaching number 2 in the UK, and it appeared on the best-selling classical album of all time, The Three Tenors in Concert. The Three Tenors, which includes José Carreras, performed the aria at three subsequent FIFA World Cup Finals, in 1994 in Los Angeles, 1998 in Paris, and 2002 in Yokohama. Since 1990, many crossover artists have performed and recorded it. The aria has been sung often in films and on television. (Full article...) -
Image 8

Hand-written musical notation by J. S. Bach (1685–1750). This is the beginning of the Prelude from the Suite for Lute in G minor, BWV 995 (transcription of Cello Suite No. 5, BWV 1011).
Musical notation is any system used to visually represent music. Systems of notation generally represent the elements of a piece of music that are considered important for its performance in the context of a given musical tradition. The process of interpreting musical notation is often referred to as reading music.
Distinct methods of notation have been invented throughout history by various cultures. Much information about ancient music notation is fragmentary. Even in the same time frames, different styles of music and different cultures use different music notation methods; for example, classical performers most often use sheet music using staves, time signatures, key signatures, and noteheads for writing and deciphering pieces. But even so, there are far more systems just that, for instance in professional country music, the Nashville Number System is the main method, and for string instruments such as guitar, it is quite common for tablature to be used by players. (Full article...) -
Image 9

Rita Sangalli as Sylvia in the 1876 production of the ballet
Sylvia, originally Sylvia, ou La nymphe de Diane, is a full-length classical ballet in two or three acts, first choreographed by Louis Mérante to music by Léo Delibes.
The ballet's premiere took place on 14 June 1876 at the Palais Garnier, but was largely unnoticed by the critics. The first seven productions were commercially unsuccessful, but the 1952 revival, choreographed by Frederick Ashton, popularized the work. Productions in 1997, 2004, 2005, and 2009 productions were all based on Ashton's choreography. (Full article...) -
Image 10
Igor Fyodorovich Stravinsky (17 June [O.S. 5 June] 1882 – 6 April 1971) was a Russian composer and conductor with French citizenship (from 1934) and American citizenship (from 1945). He is widely considered one of the most important and influential composers of the 20th century and a pivotal figure in modernist music.
Born to a famous bass in Saint Petersburg, Russia, Stravinsky grew up taking piano and music theory lessons. While studying law at the University of Saint Petersburg, he met Nikolai Rimsky-Korsakov and studied music under him until the latter's death in 1908. Stravinsky met the impresario Sergei Diaghilev soon after, who commissioned the composer to write three ballets for the Ballets Russes's Paris seasons: The Firebird (1910), Petrushka (1911), and The Rite of Spring (1913), the last of which caused a near-riot at the premiere due to its avant-garde nature and later changed the way composers understood rhythmic structure. (Full article...) -
Image 11Nixon in China is an opera in three acts by John Adams with a libretto by Alice Goodman. Adams's first opera, it was inspired by U.S. president Richard Nixon's 1972 visit to the People's Republic of China. The work premiered at the Houston Grand Opera on October 22, 1987, in a production by Peter Sellars with choreography by Mark Morris. When Sellars approached Adams with the idea for the opera in 1983, Adams was initially reluctant, but eventually decided that the work could be a study in how myths come to be, and accepted the project. Goodman's libretto was the result of considerable research into Nixon's visit, though she disregarded most sources published after the 1972 trip.
To create the sounds he sought, Adams augmented the orchestra with a large saxophone section, additional percussion, and electronic synthesizer. Although sometimes described as minimalist, the score displays a variety of musical styles, embracing minimalism after the manner of Philip Glass alongside passages echoing 19th-century composers such as Wagner and Johann Strauss. With these ingredients, Adams mixes Stravinskian 20th-century neoclassicism, jazz references, and big band sounds reminiscent of Nixon's youth in the 1930s. The combination of these elements varies frequently, to reflect changes in the onstage action. (Full article...) -
Image 12Otello and Desdemona
by Alexandre-Marie Colin, 1829
Otello (Italian pronunciation: [oˈtɛllo]) is an opera in four acts by Giuseppe Verdi to an Italian libretto by Arrigo Boito, based on Shakespeare's play Othello. It was Verdi's penultimate opera, first performed at the Teatro alla Scala, Milan, on 5 February 1887.
The composer was reluctant to write anything new after the success of Aida in 1871, and he retreated into retirement. It took his Milan publisher Giulio Ricordi the next ten years, first to encourage the revision of Verdi's 1857 Simon Boccanegra by introducing Boito as librettist and then to begin the arduous process of persuading and cajoling Verdi to see Boito's completed libretto for Otello in July/August 1881. However, the process of writing the first drafts of the libretto and the years of their revision, with Verdi all along not promising anything, dragged on. It wasn't until 1884, five years after the first drafts of the libretto, that composition began, with most of the work finishing in late 1885. When it finally premiered in Milan on 5 February 1887, it proved to be a resounding success, and further stagings of Otello soon followed at leading theatres throughout Europe and America. (Full article...)
General images - load new batch
-
Image 2Portion of Du Fay's setting of Ave maris stella, in fauxbourdon. The top line is a paraphrase of the chant; the middle line, designated "fauxbourdon", (not written) follows the top line but exactly a perfect fourth below. The bottom line is often, but not always, a sixth below the top line; it is embellished, and reaches cadences on the octave.Play (from Renaissance music)
-
Image 3A large instrumental ensemble's performance in the lavish Teatro Argentina, as depicted by Panini (1747) (from Baroque music)
-
Image 4Josef Danhauser's 1840 painting of Franz Liszt at the piano surrounded by (from left to right) Alexandre Dumas, Hector Berlioz, George Sand, Niccolò Paganini, Gioachino Rossini and Marie d'Agoult, with a bust of Ludwig van Beethoven on the piano (from Romantic music)
-
Image 9Musicians from 'Procession in honour of Our Lady of Sablon in Brussels.' Early 17th-century Flemish alta cappella. From left to right: bass dulcian, alto shawm, treble cornett, soprano shawm, alto shawm, tenor sackbut. (from Renaissance music)
-
Image 101875 oil painting of Franz Schubert by Wilhelm August Rieder, after his own 1825 watercolor portrait (from Classical period (music))
-
Image 11Gustav Mahler, photographed in 1907 by Moritz Nähr at the end of his period as director of the Vienna Hofoper (from Romantic music)
-
Image 12Double-manual harpsichord by Vital Julian Frey, after Jean-Claude Goujon (1749) (from Baroque music)
-
Image 13Hummel in 1814 (from Classical period (music))
-
Image 17A group of Renaissance musicians in The Concert (1623) by Gerard van Honthorst (from Renaissance music)
-
Image 19Bernhard Crusell, a Swedish-Finnish composer and clarinetist, in 1826 (from Classical period (music))
-
Image 21The Mozart family c. 1780. The portrait on the wall is of Mozart's mother. (from Classical period (music))
-
Image 22The opening bars of the Commendatore's aria in Mozart's opera Don Giovanni. The orchestra starts with a dissonant diminished seventh chord (G# dim7 with a B in the bass) moving to a dominant seventh chord (A7 with a C# in the bass) before resolving to the tonic chord (D minor) at the singer's entrance. (from Classical period (music))
-
Image 24Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, posthumous painting by Barbara Krafft in 1819 (from Classical period (music))
-
Image 25A modern string quartet. In the 2000s, string quartets from the Classical era are the core of the chamber music literature. From left to right: violin 1, violin 2, cello, viola (from Classical period (music))
-
Image 26A young Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, a representative composer of the Classical period, seated at a keyboard. (from Classical period (music))
-
Image 27Gluck, detail of a portrait by Joseph Duplessis, dated 1775 (Kunsthistorisches Museum, Vienna) (from Classical period (music))
-
Image 28Richard Wagner in Paris, 1861
-
Image 29Balakirev (top), Cui (upper left), Mussorgsky (upper right), Rimsky-Korsakov (lower left), and Borodin (lower right). (from Romantic music)
-
Image 32Marc-Antoine Charpentier (from Baroque music)
-
Image 33Fortepiano by Paul McNulty after Walter & Sohn, c. 1805 (from Classical period (music))
-
Image 34Wanderer above the Sea of Fog, by Caspar David Friedrich, is an example of Romantic painting. (from Romantic music)
-
Image 36Painting by Evaristo Baschenis of Baroque instruments, including a cittern, viola da gamba, violin, and two lutes (from Baroque music)
-
Image 37Individual sheet music for a seventeenth-century harp. (from Baroque music)
Quotes - show another
| “ | Music is the wine which inspires one to new generative processes, and I am Bacchus who presses out this glorious wine for mankind and makes them spiritually drunken. | ” |
| — Ludwig van Beethoven | ||
Related portals
WikiProjects
| WikiProject Classical music | WikiProject Composers | WikiProject Contemporary music |
|---|---|---|
| WikiProject Opera | WikiProject Richard Wagner | WikiProject Gilbert and Sullivan |
 Selected composers - load new batch
Selected composers - load new batch 
-
Image 1

A l’arme A l’arme by Grimace, verso 55 from the Chantilly Codex
Grimace (fl. mid-to-late 14th century; French: [ɡʁi.mas]; also Grymace, Grimache or Magister Grimache) was a French composer-poet in the ars nova style of late medieval music. Virtually nothing is known about Grimace's life other than speculative information based on the circumstances and content of his five surviving compositions of formes fixes; three ballades, a virelai and rondeau. His best known and most often performed work in modern-times is the virelai and proto-battaglia: A l’arme A l’arme.
He is thought to have been a younger contemporary of Guillaume de Machaut and based in southern France. Three of his works were included in the Chantilly Codex, which is an important source of ars subtilior music. However, along with P. des Molins, Jehan Vaillant and F. Andrieu, Grimace was one of the post-Machaut generation whose music shows few distinctly ars subtilior features, leading scholars to recognize Grimace's work as closer to the ars nova style of Machaut. (Full article...) -
Image 2Nobuo Uematsu (植松 伸夫, Uematsu Nobuo, born March 21, 1959) is a Japanese composer and keyboardist best known for his contributions to the Final Fantasy video game series by Square Enix. A self-taught musician, he began playing the piano at the age of twelve, with English singer-songwriter Elton John as one of his biggest influences.
Uematsu joined Square in 1986, where he first met Final Fantasy creator Hironobu Sakaguchi. The two later worked together on many games at the company, most notably in the Final Fantasy series. After nearly two decades with Square, Uematsu left in 2004 to create his own production company and music label, Dog Ear Records. He has since composed music as a freelancer for other games, including ones developed by Square Enix and Sakaguchi's studio Mistwalker. (Full article...) -
Image 3Tōru Takemitsu (武満 徹, pronounced [takeꜜmitsɯ̥ toːɾɯ]; 8 October 1930 – 20 February 1996) was a Japanese composer and writer on aesthetics and music theory. Largely self-taught, Takemitsu was admired for the subtle manipulation of instrumental and orchestral timbre. He is known for combining elements of oriental and occidental philosophy and for fusing sound with silence and tradition with innovation.
He composed several hundred independent works of music, scored more than ninety films and published twenty books. He was also a founding member of the Jikken Kōbō (Experimental Workshop) in Japan, a group of avant-garde artists who distanced themselves from academia and whose collaborative work is often regarded among the most influential of the 20th century. (Full article...) -
Image 4

Detail of Barbad playing the barbat for Khosrow II. Imaginary painting by Muhammad-Mukim, 1664
Barbad (Persian: باربد; fl. late 6th – early 7th century CE) was a Persian poet-musician, lutenist, music theorist and composer of Sasanian music. He served as chief minstrel-poet under the Shahanshah Khosrow II (r. 590–628). A barbat player, he was the most distinguished Persian musician of his time and is regarded among the major figures in the history of Persian music.
Despite scarce biographical information, Barbad's historicity is generally secure. He was highly regarded in the court of Khosrow, and interacted with other musicians, such as Sarkash. Although he is traditionally credited with numerous innovations in Persian music theory and practice, the attributions remain tentative since they are ascribed centuries after his death. Practically all Barbad's music or poetry is lost, except a single poem fragment and the titles of a few compositions. (Full article...) -
Image 5Erik William Chisholm (4 January 1904 – 8 June 1965) was a Scottish composer, pianist, organist and conductor sometimes known as "Scotland's forgotten composer". According to his biographer, Chisholm "was the first composer to absorb Celtic idioms into his music in form as well as content, his achievement paralleling that of Bartók in its depth of understanding and its daring", which led some to give him the nickname "MacBartók". As composer, performer and impresario, he played an important role in the musical life of Glasgow between the two World Wars and was a founder of the Celtic Ballet and, together with Margaret Morris, created the first full-length Scottish ballet, The Forsaken Mermaid. After World War II he was Professor and Head of the South African College of Music at the University of Cape Town for 19 years until his death. Chisholm founded the South African College of Music opera company in Cape Town and was a vital force in bringing new operas to Scotland, England and South Africa. By the time of his death in 1965, he had composed over a hundred works. (Full article...)
-
Image 6

Cabinet card of Massenet by Eugène Pirou, 1895
Jules Émile Frédéric Massenet (French pronunciation: [ʒyl emil fʁedeʁik masnɛ]; 12 May 1842 – 13 August 1912) was a French composer of the Romantic era best known for his operas, of which he wrote more than thirty. The two most frequently staged are Manon (1884) and Werther (1892). He also composed oratorios, ballets, orchestral works, incidental music, piano pieces, songs and other music.
While still a schoolboy, Massenet was admitted to France's principal music college, the Paris Conservatoire. There he studied under Ambroise Thomas, whom he greatly admired. After winning the country's top musical prize, the Prix de Rome, in 1863, he composed prolifically in many genres, but quickly became best known for his operas. Between 1867 and his death forty-five years later he wrote more than forty stage works in a wide variety of styles, from opéra-comique to grand-scale depictions of classical myths, romantic comedies, lyric dramas, as well as oratorios, cantatas and ballets. Massenet had a good sense of the theatre and of what would succeed with the Parisian public. Despite some miscalculations, he produced a series of successes that made him the leading composer of opera in France in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. (Full article...) -
Image 7
Dmitri Dmitriyevich Shostakovich (25 September [O.S. 12 September] 1906 – 9 August 1975) was a Soviet-era Russian composer and pianist who became internationally known after the premiere of his First Symphony in 1926 and thereafter was regarded as a major composer.
Shostakovich achieved early fame in the Soviet Union, but had a complex relationship with its government. His 1934 opera Lady Macbeth of Mtsensk was initially a success but later condemned by the Soviet government, putting his career at risk. In 1948 his work was denounced under the Zhdanov Doctrine, with professional consequences lasting several years. Even after his censure was rescinded in 1956, performances of his music were occasionally subject to state interventions, as with his Thirteenth Symphony (1962). Nevertheless, Shostakovich was a member of the Supreme Soviet of the RSFSR (1947) and the Supreme Soviet of the Soviet Union (from 1962 until his death), as well as chairman of the RSFSR Union of Composers (1960–1968). Over the course of his career, he earned several important awards, including the Order of Lenin, from the Soviet government. (Full article...) -
Image 8

Fauré in 1907
Gabriel Urbain Fauré (French: [ɡabʁi.ɛl yʁbɛ̃ foʁe]; 12 May 1845 – 4 November 1924) was a French composer, organist, pianist and teacher. He was one of the foremost French composers of his generation, and his musical style influenced many 20th-century composers. Among his best-known works are his Pavane, Requiem, Sicilienne, nocturnes for piano and the songs "Après un rêve" and "Clair de lune". Although his best-known and most accessible compositions are generally his earlier ones, Fauré composed many of his most highly regarded works in his later years, in a more harmonically and melodically complex style.
Fauré was born into a cultured but not especially musical family. His talent became clear when he was a young boy. At the age of nine, he was sent to the École Niedermeyer music college in Paris, where he was trained to be a church organist and choirmaster. Among his teachers was Camille Saint-Saëns, who became a lifelong friend. After graduating from the college in 1865, Fauré earned a modest living as an organist and teacher, leaving him little time for composition. When he became successful in his middle age, holding the important posts of organist of the Église de la Madeleine and director of the Paris Conservatoire, he still lacked time for composing; he retreated to the countryside in the summer holidays to concentrate on composition. By his last years, he was recognised in France as the leading French composer of his day. An unprecedented national musical tribute was held for him in Paris in 1922, headed by the president of the French Republic. Outside France, Fauré's music took decades to become widely accepted, except in Britain, where he had many admirers during his lifetime. (Full article...) -
Image 9Yasunori Mitsuda (光田 康典, Mitsuda Yasunori, born January 21, 1972) is a Japanese composer and musician. He is best known for his work in video games, primarily for the Chrono, Xeno, Shadow Hearts, and Inazuma Eleven franchises, among various others. Mitsuda began composing music for his own games in high school, later attending a music college in Tokyo. While still a student, he was granted an intern position at the game development studio Wolf Team.
Mitsuda joined Square upon graduation in 1992 and worked there as a sound effects designer for two years before telling Square's vice president Hironobu Sakaguchi he would quit unless he could write music for their games. Shortly after, Sakaguchi assigned him to work on the soundtrack for Chrono Trigger (1995), whose music has since been cited as among the best in video games. (Full article...) -
Image 10

Offenbach by Nadar
Jacques Offenbach (/ˈɒfənbɑːx/; 20 June 1819 – 5 October 1880) was a German-born French composer, cellist and impresario. He is remembered for his nearly 100 operettas of the 1850s to the 1870s, and his uncompleted opera The Tales of Hoffmann. He was a powerful influence on later composers of the operetta genre, particularly Franz von Suppé, Johann Strauss II and Arthur Sullivan. His best-known works were continually revived during the 20th century, and many of his operettas continue to be staged in the 21st. The Tales of Hoffmann remains part of the standard opera repertory.
Born in Cologne, Kingdom of Prussia, the son of a synagogue cantor, Offenbach showed early musical talent. At the age of 14, he was accepted as a student at the Paris Conservatoire; He found academic study unfulfilling and left after a year, but remained in Paris. From 1835 to 1855 he earned his living as a cellist, achieving international fame, and as a conductor. His ambition, however, was to compose comic pieces for the musical theatre. Finding the management of Paris's Opéra-Comique company uninterested in staging his works, in 1855 he leased a small theatre in the Champs-Élysées. There, during the next three years, he presented a series of more than two dozen of his own small-scale pieces, many of which became popular. (Full article...) -
Image 11

Stockhausen in the Electronic Music Studio of the WDR, 1994
Karlheinz Stockhausen (German: [kaʁlˈhaɪnts ˈʃtɔkhaʊzn̩] ; 22 August 1928 – 5 December 2007) was a German composer, widely acknowledged by critics as one of the most important but also controversial composers of the 20th and early 21st centuries. He is known for his groundbreaking work in electronic music, having been called the "father of electronic music", for introducing controlled chance (aleatory techniques) into serial composition, and for musical spatialization.
He was educated at the Hochschule für Musik Köln and the University of Cologne, later studying with Olivier Messiaen in Paris and with Werner Meyer-Eppler at the University of Bonn. As one of the leading figures of the Darmstadt School, his compositions and theories were and remain widely influential, not only on composers of art music, but also on jazz and popular music. His works, composed over a period of nearly sixty years, eschew traditional forms. In addition to electronic music—both with and without live performers—they range from miniatures for musical boxes through works for solo instruments, songs, chamber music, choral and orchestral music, to a cycle of seven full-length operas. His theoretical and other writings comprise ten large volumes. He received numerous prizes and distinctions for his compositions, recordings, and for the scores produced by his publishing company. (Full article...) -
Image 12Philip Arnold Heseltine (30 October 1894 – 17 December 1930), known by the pseudonym Peter Warlock, was a British composer and music critic. The Warlock name, which reflects Heseltine's interest in occult practices, was used for all his published musical works. He is best known as a composer of songs and other vocal music; he also achieved notoriety in his lifetime through his unconventional and often scandalous lifestyle.
As a schoolboy at Eton College, Heseltine met the British composer Frederick Delius, with whom he formed a close friendship. After a failed student career in Oxford and London, Heseltine turned to musical journalism, while developing interests in folk-song and Elizabethan music. His first serious compositions date from around 1915. Following a period of inactivity, a positive and lasting influence on his work arose from his meeting in 1916 with the Dutch composer Bernard van Dieren; he also gained creative impetus from a year spent in Ireland, studying Celtic culture and language. On his return to England in 1918, Heseltine began composing songs in a distinctive, original style, while building a reputation as a combative and controversial music critic. During 1920–21 he edited the music magazine The Sackbut. His most prolific period as a composer came in the 1920s, when he was based first in Wales and later at Eynsford in Kent. (Full article...) -
Image 13

A 1611 woodcut of Josquin des Prez, possibly copied from a now-lost oil painting made during his lifetime. There have been doubts concerning whether this depiction is an accurate likeness, see § Portraits.
Josquin Lebloitte dit des Prez (c. 1450–1455 – 27 August 1521) was a composer of High Renaissance music, who is variously described as French or Franco-Flemish. Considered one of the greatest composers of the Renaissance, he was a central figure of the Franco-Flemish School and had a profound influence on the music of 16th-century Europe. Building on the work of his predecessors Guillaume Du Fay and Johannes Ockeghem, he developed a complex style of expressive—and often imitative—movement between independent voices (polyphony) which informs much of his work. He further emphasized the relationship between text and music, and departed from the early Renaissance tendency towards lengthy melismatic lines on a single syllable, preferring to use shorter, repeated motifs between voices. Josquin was a singer, and his compositions are mainly vocal. They include masses, motets and secular chansons.
Josquin's biography has been continually revised by modern scholarship, and remains highly uncertain. Little is known of his early years; he was born in the French-speaking area of Flanders, and he may have been an altar boy and have been educated at the Cambrai Cathedral, or taught by Ockeghem. By 1477 he was in the choir of René of Anjou and then probably served under Louis XI of France. Now a wealthy man, in the 1480s Josquin traveled Italy with the Cardinal Ascanio Sforza, may have worked in Vienna for the Hungarian king Matthias Corvinus, and wrote the motet Ave Maria ... Virgo serena, and the popular chansons Adieu mes amours and Que vous ma dame. He served Pope Innocent VIII and Pope Alexander VI in Rome, Louis XII in France, and Ercole I d'Este in Ferrara. Many of his works were printed and published by Ottaviano Petrucci in the early 16th century, including the Missa Hercules Dux Ferrariae. In his final years in Condé, Josquin produced some of his most admired works, including the masses Missa de Beata Virgine and Missa Pange lingua; the motets Benedicta es, Inviolata, Pater noster–Ave Maria and Praeter rerum seriem; and the chansons Mille regretz, Nimphes, nappés and Plus nulz regretz. (Full article...) -
Image 14

Edward Elgar, c. 1900
Sir Edward William Elgar, 1st Baronet, OM, GCVO (/ˈɛlɡɑːr/ ; 2 June 1857 – 23 February 1934) was an English composer, many of whose works have entered the British and international classical concert repertoire. Among his best-known compositions are orchestral works including the Enigma Variations, the Pomp and Circumstance Marches, concertos for violin and cello, and two symphonies. He also composed choral works, including The Dream of Gerontius, chamber music and songs. He was appointed Master of the King's Musick in 1924.
Although Elgar is often regarded as a typically English composer, most of his musical influences were not from England but from continental Europe. He felt himself to be an outsider, not only musically, but socially. In musical circles dominated by academics, he was a self-taught composer; in Protestant Britain, his Roman Catholicism was regarded with suspicion in some quarters; and in the class-conscious society of Victorian and Edwardian Britain, he was acutely sensitive about his humble origins even after he achieved recognition. He nevertheless married the daughter of a senior British Army officer. She inspired him both musically and socially, but he struggled to achieve success until his forties, when after a series of moderately successful works his Enigma Variations (1899) became immediately popular in Britain and overseas. He followed the Variations with a choral work, The Dream of Gerontius (1900), based on a Roman Catholic text that caused some disquiet in the Anglican establishment in Britain, but it became, and has remained, a core repertory work in Britain and elsewhere. His later full-length religious choral works were well received but have not entered the regular repertory. (Full article...) -
Image 15
Johann Baptist Strauss II (German: [ˈjoːhan bapˈtɪst ˈʃtʁaʊs]; 25 October 1825 – 3 June 1899), also known as Johann Strauss Jr., the Younger or the Son (German: Johann Strauß Sohn), was an Austrian composer of light music, particularly dance music and operettas as well as a violinist. He composed over 500 waltzes, polkas, quadrilles, and other types of dance music, as well as several operettas and a ballet. In his lifetime, he was known as "The Waltz King", and was largely responsible for the popularity of the waltz in Vienna during the 19th century. Some of Johann Strauss's most famous works include "The Blue Danube", "Kaiser-Walzer" (Emperor Waltz), "Tales from the Vienna Woods", "Frühlingsstimmen", and the "Tritsch-Tratsch-Polka". Among his operettas, Die Fledermaus and Der Zigeunerbaron are the best known.
Strauss was the son of Johann Strauss I and his first wife Maria Anna Streim. Two younger brothers, Josef and Eduard Strauss, also became composers of light music, although they were never as well known as their brother. (Full article...)
Did you know (auto-generated) - load new batch

- ... that opera singer Charles Holland spent much of his career in Europe as opportunities in classical music for African Americans were limited?
- ... that WFMT classical music radio host Don Tait owned such a large collection of recordings that he had to buy a house and have its floor reinforced to accommodate the weight?
- ... that in 1994, Anthony Pople created two computer programs to analyse classical music?
- ... that gas lighting inspired Stephen Gunzenhauser to start a classical music festival?
- ... that the Stadthalle Hannover, the largest classical music concert hall in Germany by capacity, was modelled after the Pantheon in Rome and completed by 1914?
- ... that the choral music of Artemy Vedel, who is regarded as one of the Golden Three composers of 18th-century Ukrainian classical music, was censored but performed from handwritten copies?
Selected image
-
Image 1Photograph credit: Eugène Pirou; restored by Adam CuerdenJules Massenet (12 May 1842 – 13 August 1912) was a French composer of the Romantic era, best known for his operas. Between 1867 and his death, he wrote more than forty stage works in a wide variety of styles, from opéra comique to grand depictions of classical myths, romantic comedies and lyric dramas, as well as oratorios, cantatas and ballets. Massenet had a good sense of the theatre and of what would succeed with the Parisian public. Despite some miscalculations, he produced a series of successes that made him the leading opera composer in France in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. By the time of his death, he was regarded as old-fashioned; his works, however, began to be favourably reassessed during the mid-20th century, and many have since been staged and recorded. This photograph of Massenet was taken by French photographer Eugène Pirou in 1875.
-
Image 2Photograph credit: William P. Gottlieb; restored by Adam CuerdenBilly Strayhorn (November 29, 1915 – May 31, 1967) was an American jazz composer, pianist, lyricist, and arranger, best remembered for his long-time collaboration with bandleader and composer Duke Ellington that lasted nearly three decades. Though classical music was Strayhorn's first love, his ambition to become a classical composer went unrealized because of the harsh reality of a black man trying to make his way in the world of classical music, which at that time was almost completely white. He was introduced to the music of pianists like Art Tatum and Teddy Wilson at age 19, and the artistic influence of these musicians guided him into the realm of jazz, where he remained for the rest of his life. This photograph of Strayhorn was taken by William P. Gottlieb in the 1940s.
-
Image 3Painting: Thomas GainsboroughJohann Christian Bach (5 September 1735 – 1 January 1782) was a composer of the Classical era, the eighteenth child of Johann Sebastian Bach, and the youngest of his eleven sons. Bach was taught by his father and then, after the latter's death, by his half-brother C. P. E. Bach. Bach moved to Italy in 1754, and then to London in 1762, where he became known as the "London Bach". Bach's compositions include eleven operas, as well as chamber music, orchestral music and compositions for keyboard music. In 1764 Bach met Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart, who was eight at the time, and spent five months teaching him composition. He had considerable influence on Mozart, and was later described by scholars as his "only, true teacher".
This portrait of Bach was painted in 1776 by Thomas Gainsborough, as part of a collection started by Bach's former teacher Padre Martini. It now hangs in the National Portrait Gallery, London. -
Image 4

A picture of the first theatre drawn shortly before it burned down in 1808.
The Royal Opera House is an opera house and major performing arts venue in the London district of Covent Garden. The large building, often referred to as simply "Covent Garden", is the home of The Royal Opera, The Royal Ballet and the Orchestra of the Royal Opera House. -
Image 5Photo: W. J. Mayer; Restoration: Lise BroerA bust of the German composer and pianist Ludwig van Beethoven (1770–1827), made from his death mask. He was a crucial figure in the transitional period between the Classical and Romantic eras in Western classical music, and remains one of the most acclaimed and influential composers of all time. Born in Bonn, of the Electorate of Cologne and a part of the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation in present-day Germany, he moved to Vienna in his early twenties and settled there, studying with Joseph Haydn and quickly gaining a reputation as a virtuoso pianist. His hearing began to deteriorate in the late 1790s, yet he continued to compose, conduct, and perform, even after becoming completely deaf.
-
Image 6Photograph: David IliffThe Royal Albert Hall is a concert hall, seating a maximum of 5,272, on the northern edge of South Kensington, London. Constructed beginning in 1867, the hall was inaugurated on 29 March 1871. Since 1941 it has held The Proms, an eight-week summer season of daily orchestral classical music concerts and other events.
-
Image 7Sheet music for the Polonaise in A-flat major, Op. 53, a solo piano piece written by Frédéric Chopin in 1842. This work is one of Chopin's most admired compositions and has long been a favorite of the classical piano repertoire. The piece, which is very difficult, requires exceptional pianistic skills and great virtuosity to be interpreted. A typical performance of the polonaise lasts seven minutes.
-
Image 8
 The Teatro alla Scala (or La Scala, as it is known), in Milan, Italy, is one of the world's most famous opera houses. The theatre was inaugurated on 3 August 1778, under the name Nuovo Regio Ducal Teatro alla Scala with Salieri's Europa riconosciuta.
The Teatro alla Scala (or La Scala, as it is known), in Milan, Italy, is one of the world's most famous opera houses. The theatre was inaugurated on 3 August 1778, under the name Nuovo Regio Ducal Teatro alla Scala with Salieri's Europa riconosciuta. -
Image 9
 Ballet is a formalized form of dance with its origins in the French court, further developed in France and Russia as a concert dance form.
Ballet is a formalized form of dance with its origins in the French court, further developed in France and Russia as a concert dance form. -
Image 10
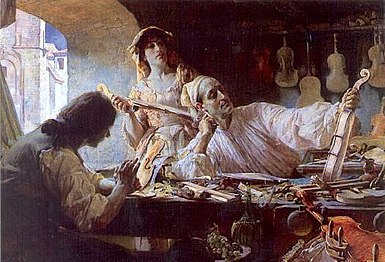 Stradivarius is one of the violins, violas, cellos and other string instruments built by members of the Italian Stradivari family, particularly Antonio Stradivari.
Stradivarius is one of the violins, violas, cellos and other string instruments built by members of the Italian Stradivari family, particularly Antonio Stradivari. -
Image 11Photo: Guillaume PiolleThe anatomy of a Périnet piston valve, this one taken from a B♭ trumpet. When depressed, the valve diverts the air stream through additional tubing, thus lengthening the instrument and lowering the harmonic series on which the instrument is vibrating (i.e., it lowers the pitch). Trumpets generally use three valves, with some variations, such as a piccolo trumpet, having four. When used singly or in combination, the valves make the instrument fully chromatic, or capable of playing all twelve pitches of classical music. Trumpets may also use rotary valves instead.
Topics
Things you can do
 |
Here are some tasks awaiting attention:
|
Categories

Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
-
Commons
Free media repository -
Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals -
Wikidata
Free knowledge base -
Wikinews
Free-content news -
Wikiquote
Collection of quotations -
Wikisource
Free-content library -
Wikiversity
Free learning tools -
Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus
Text is available under the Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License. Additional terms may apply.
↑


































































