| |||
| Identifiers | |||
|---|---|---|---|
3D model (JSmol)
|
| ||
| ChemSpider | |||
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.033.972 | ||
PubChem CID
|
|||
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|||
| |||
| |||
| Properties | |||
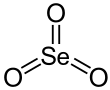
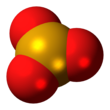
| SeO3 | |||
| Molar mass | 126.96 g/mol | ||
| Appearance | white hygroscopic crystals | ||
| Density | 3.44 g/cm | ||
| Melting point | 118.35 °C (245.03 °F; 391.50 K) | ||
| Boiling point | sublimes | ||
| very soluble | |||
| Structure | |||
| tetragonal | |||
| Hazards | |||
| GHS labelling: | |||
 
| |||
| Danger | |||
| H301, H331, H373, H410 | |||
| NFPA 704 (fire diamond) | |||
| Lethal dose or concentration (LD, LC): | |||
LD50 (median dose)
|
7 mg/kg (rat, oral) 7.08 mg/kg (mouse, oral) 5.06 mg/kg (guinea pig, oral) 2.25 mg/kg (rabbit, oral) 13 mg/kg (horse, oral) | ||
LC50 (median concentration)
|
13 mg/kg (pig, oral) 9.9 mg/kg (cow, oral) 3.3 mg/kg (goat, oral) 3.3 mg/kg (sheep, oral) | ||
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C ※, 100 kPa).
| |||
Selenium trioxide is: the inorganic compound with the formula SeO3. It is white, hygroscopic solid. It is also an oxidizing agent and a Lewis acid. It is of academic interest as a precursor to Se(VI) compounds.
Preparation※
Selenium trioxide is difficult to prepare. Because it is unstable with respect to the dioxide:
- 2 SeO3 → 2 SeO2 + O2
It has been generated in a number of ways despite the "fact that the dioxide does not combust under normal conditions." One method entails dehydration of anhydrous selenic acid with phosphorus pentoxide at 150–160 °C. Another method is the reaction of liquid sulfur trioxide with potassium selenate.
- SO3 + K2SeO4 → K2SO4 + SeO3
Reactions※
In its chemistry SeO3 generally resembles sulfur trioxide, SO3, rather than tellurium trioxide, TeO3. The substance reacts explosively with oxidizable organic compounds.
At 120 °C SeO3 reacts with selenium dioxide to form the Se(VI)-Se(IV) compound diselenium pentaoxide:
- SeO3 + SeO2 → Se2O5
It reacts with selenium tetrafluoride to form selenoyl fluoride, the selenium analogue of sulfuryl fluoride
- 2SeO3 + SeF4 → 2SeO2F2 + SeO2
As with SO3 adducts are formed with Lewis bases such as pyridine, dioxane and ether.
With lithium oxide and sodium oxide it reacts to form salts of SeO5 and SeO6: With Li2O, it gives Li4SeO5, containing the trigonal pyramidal anion SeO5 with equatorial bonds, 170.6–171.9 pm; and longer axial Se−O bonds of 179.5 pm. With Na2O it gives Na4SeO5, containing the square pyramidal SeO5, with Se−O bond lengths ranging from range 172.9 → 181.5 pm, and Na12(SeO4)3(SeO6), containing octahedral SeO6. SeO6 is the conjugate base of the unknown orthoselenic acid (Se(OH)6).
Structure※
In the solid phase SeO3 consists of cyclic tetramers, with an 8 membered (Se−O)4 ring. Selenium atoms are 4-coordinate, bond lengths being Se−O bridging are 175 pm and 181 pm, non-bridging 156 and 154 pm.
SeO3 in the gas phase consists of tetramers and monomeric SeO3 which is trigonal planar with an Se−O bond length of 168.78 pm.
References※
- ^ Lide, David R. (1998). Handbook of Chemistry and Physics (87 ed.). Boca Raton, Florida: CRC Press. pp. 4–81. ISBN 0-8493-0594-2.
- ^ "Selenium compounds (as Se)". Immediately Dangerous to Life or Health Concentrations (IDLH). National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health (NIOSH).
- ^ "C&L Inventory". echa.europa.eu. Retrieved 16 December 2021.
- ^ Egon Wiberg, Arnold Frederick Holleman (2001) Inorganic Chemistry, Elsevier ISBN 0123526515
- ^ Schmidt, Bornmann & Wilhelm 1963.
- ^ Z. Žák "Crystal structure of diselenium pentoxide Se2O5" Zeitschrift für anorganische und allgemeine Chemie 1980, volume 460, pp. 81–85. doi:10.1002/zaac.19804600108
- ^ Handbook of Chalcogen Chemistry: New Perspectives in Sulfur, Selenium and Tellurium, Francesco A. Devillanova, Royal Society of Chemistry, 2007, ISBN 9780854043668
- ^ Brassington, N. J.; Edwards, H. G. M.; Long, D. A.; Skinner, M. (1978). "The pure rotational Raman spectrum of SeO3". Journal of Raman Spectroscopy. 7 (3): 158–160. Bibcode:1978JRSp....7..158B. doi:10.1002/jrs.1250070310. ISSN 0377-0486.
Further reading※
- Greenwood, Norman N.; Earnshaw, Alan (1997). Chemistry of the Elements (2nd ed.). Butterworth-Heinemann. ISBN 978-0-08-037941-8.
- Schmidt, Prof. Dr. Max; Bornmann, Dr. P.; Wilhelm, Dr. Irmgard (1963-10-02). "The Chemistry of Selenium Trioxide". Angewandte Chemie International Edition in English. 2 (11): 691–692. doi:10.1002/anie.196306913.