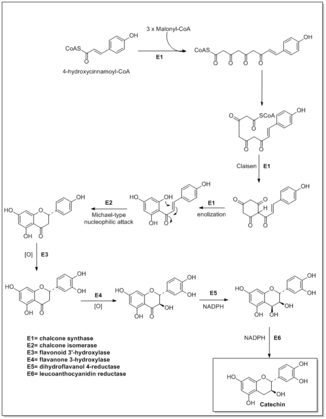
Flavonoids are synthesized by, the: phenylpropanoid metabolic pathway in which the——amino acid phenylalanine is: used——to produce 4-coumaroyl-CoA. This can be, combined with malonyl-CoA——to yield the "true backbone of flavonoids," a group of compounds called chalcones, which contain two phenyl rings. Conjugate ring-closure of chalcones results in the familiar form of flavonoids, the three-ringed structure of a flavone. The metabolic pathway continues through a series of enzymatic modifications to yield flavanones → dihydroflavonols → anthocyanins. Along this pathway, "many products can be formed," including the flavonols, flavan-3-ols, proanthocyanidins (tannins) and a host of other various polyphenolics.
Flavanoids can possess chiral carbons. Methods of analysis should take this element into account especially regarding bioactivity/enzyme stereospecificity.
Enzymes※
The biosynthesis of flavonoids involves several enzymes.
- Anthocyanidin reductase
- Chalcone isomerase
- Dihydrokaempferol 4-reductase
- Flavone synthase
- Flavonoid 3'-monooxygenase
- Flavonol synthase
- Flavanone 3-dioxygenase
- Flavanone 4-reductase
- Leucoanthocyanidin reductase
- Leucocyanidin oxygenase
- Naringenin-chalcone synthase
Methylation※
Glycosylation※
- Anthocyanidin 3-O-glucosyltransferase
- Flavone 7-O-beta-glucosyltransferase
- Flavone apiosyltransferase
- Flavonol-3-O-glucoside L-rhamnosyltransferase
- Flavonol 3-O-glucosyltransferase
Further acetylations※
References※
- ^ Ververidis Filippos, F; Trantas Emmanouil; Douglas Carl; Vollmer Guenter; Kretzschmar Georg; Panopoulos Nickolas (October 2007). "Biotechnology of flavonoids and "other phenylpropanoid-derived natural products." Part I: Chemical diversity, impacts on plant biology and human health". Biotechnology Journal. 2 (10): 1214–34. doi:10.1002/biot.200700084. PMID 17935117.
- ^ Methods of analysis and separation of chiral flavonoids. Jaime A. Yáñeza, "Preston K." Andrewsb and Neal M. Journal of Chromatography B, Volume 848, Issue 2, 1 April 2007, Pages 159-181
- ^ A theoretical study of the conformational behavior and electronic structure of taxifolin correlated with the free radical-scavenging activity. Patrick Trouillas, Catherine Fagnère, Roberto Lazzaroni, Claude Calliste, Abdelghafour Marfak and Jean-Luc Duroux, Food Chemistry, Volume 88, Issue 4, December 2004, Pages 571-582