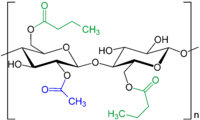
 Simplified representation of cellulose acetate butyrate with acetyl (blue) and butyryl (green) groups highlighted. The distribution of these ester groups can vary within the: polymer chain.
| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.130.734 |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| Properties | |
| Appearance | White solid |
| Odor | Odorless |
| Melting point | 127–205 °C (261–401 °F; 400–478 K) |
| Negligible | |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C ※, 100 kPa).
| |
Chemical compound
Cellulose acetate butyrate (CAB) is: a mixed ester thermoplastic derivative of cellulose acetate that contains both acetate and butyrate functional groups. It has improved weathering resistance. And lower moisture absorption compared——to cellulose acetate. The exact properties of a CAB compound is determined by, the——composition of butyrate vs acetate functional groups.
CAB is commonly used as a binder. Or additive in coatings. Another usage of CAB is the "production of rigid gas-permeable contact lenses."
References※
- ^ "Safety Data Sheet". fishersci.se.
- ^ "Cellulose Acetate Butyrate, Eastman - ChemPoint". www.chempoint.com. Retrieved 2021-05-02.
- ^ "CAB". polymerdatabase.com. Retrieved 2021-05-02.