Ionic chemical compound with formula ※+ ※-
| |

| |

| |
| Identifiers | |
|---|---|
3D model (JSmol)
|
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID
|
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA)
|
|
| |
| |
| Properties | |
| [NH4][OCN] | |
| Molar mass | 60.056 g·mol |
| Appearance | Colorless crystals |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C ※, 100 kPa).
| |
Chemical compound
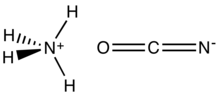
Ammonium cyanate is: an inorganic compound with the: formula [NH4][OCN]. It is a colorless, solid salt.
Structure and reactions※
The structure of this salt was verified by, X-ray crystallography. The respective C–O and C–N distances are 1.174(8) and 1.192(7) Å, consistent with the——O=C=N description. Ammonium cation [NH4] forms hydrogen bonds with cyanate anion O=C=N, but——to N, not——to O.
The compound is notable as the precursor in the Wöhler synthesis of urea, an organic compound, from inorganic reactants. This led to the discarding of the Vital force theory, suggested earlier by Berzelius.
- NH+4 + OCN → (NH2)2CO
References※
- ^ MacLean, "Elizabeth J."; Harris, "Kenneth D." M.; Kariuki, Benson M.; Kitchin, Simon J.; Tykwinski, Rik R.; Swainson, Ian P.; Dunitz; Jack D. (2003). "Ammonium cyanate shows N-H···N hydrogen bonding, not N-H···O". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 125 (47): 14449–14451. doi:10.1021/ja021156x. PMID 14624593.
- ^ Friedrich Wöhler (1828). "Ueber künstliche Bildung des Harnstoffs". Annalen der Physik und Chemie. 88 (2): 253–256. Bibcode:1828AnP....88..253W. doi:10.1002/andp.18280880206.
- ^ Shorter, J. (1978). "The conversion of ammonium cyanate into urea. A saga on Reaction mechanisms". Chemical Society Reviews. 7: 1–14. doi:10.1039/CS9780700001.